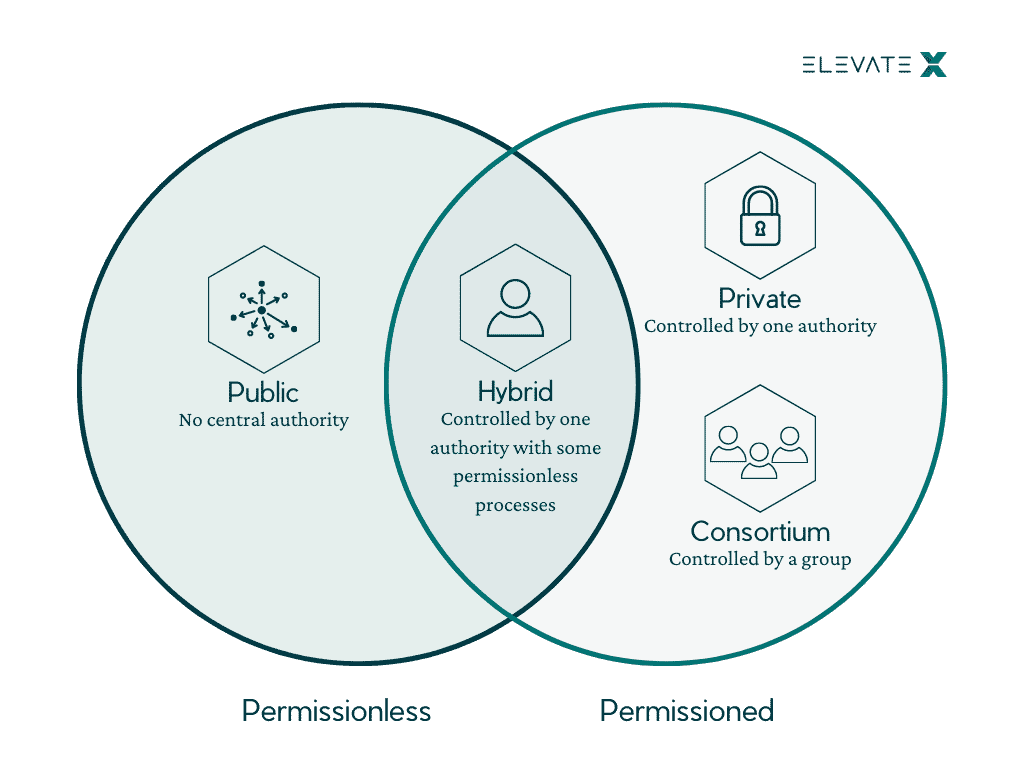
Exploring the Impact of Green IoT Solar
The Rise of Green IoT
In recent years, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology with renewable energy solutions has ushered in a new era of sustainability. Green IoT, specifically in the context of solar energy, is revolutionizing the way we generate, monitor, and manage renewable power sources. This innovative approach combines the principles of environmental responsibility with cutting-edge IoT technology to create smarter, more efficient solar energy systems.
Harnessing the Power of Solar Energy
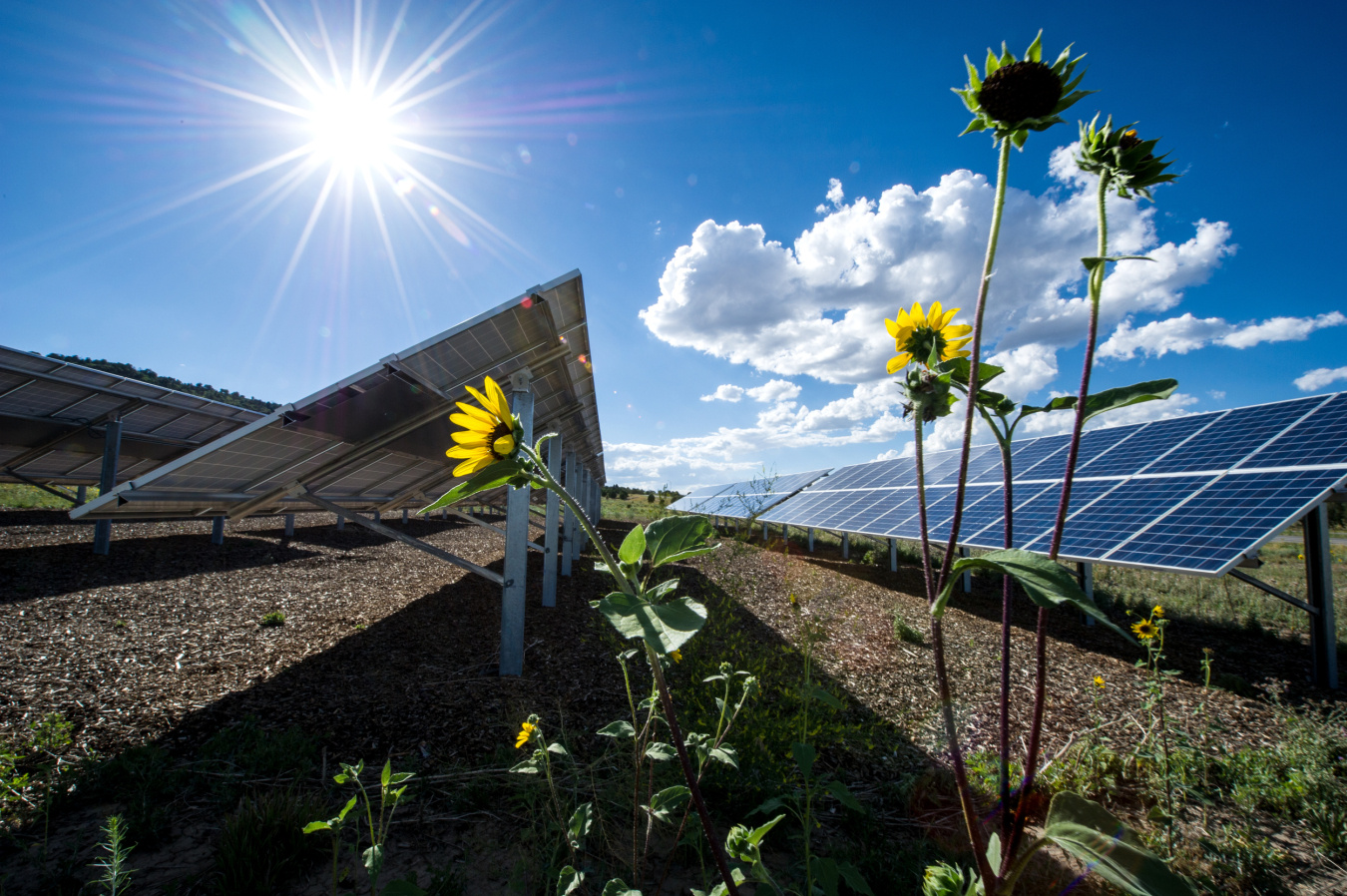
Solar energy has long been recognized as one of the most abundant and environmentally friendly sources of renewable energy. By harnessing the power of sunlight, solar panels generate electricity with minimal environmental impact, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Green IoT solar takes this a step further by integrating IoT sensors, connectivity, and data analytics to optimize solar energy production and consumption.
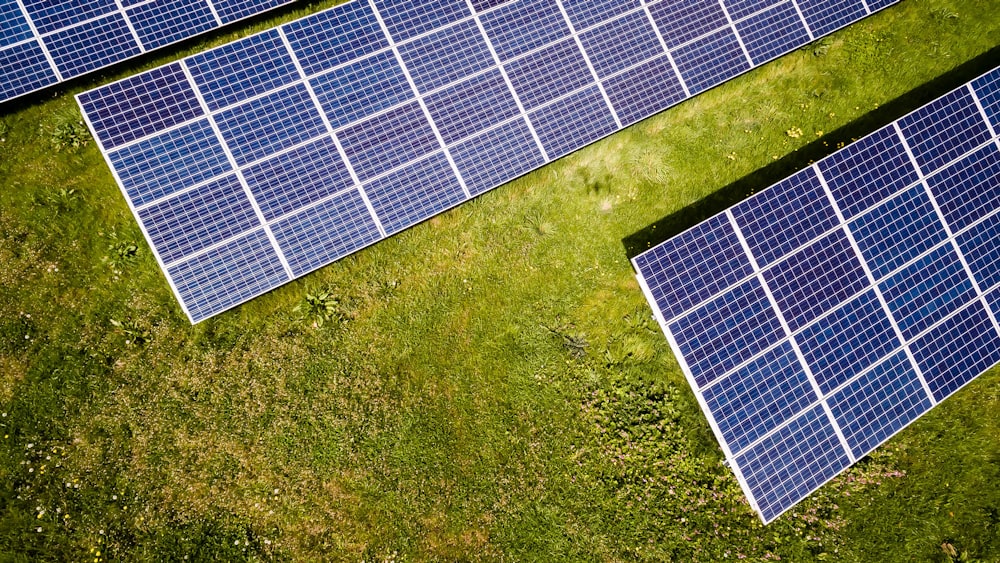
Smart Solar Monitoring Systems
Central to the concept of green IoT solar are smart monitoring systems that provide real-time insights into solar energy generation and usage. IoT sensors installed on solar panels, inverters, and other components collect data on energy production, weather conditions, and system performance. This data is then transmitted to a centralized platform where it is analyzed and used to optimize solar energy production, detect issues, and improve overall system efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance and Fault Detection
One of the key benefits of green IoT solar is its ability to enable predictive maintenance and fault detection in solar energy systems. By analyzing data from IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms can identify potential issues before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This predictive approach helps ensure the reliability and longevity of solar installations, maximizing their lifespan and return on investment.
Optimized Energy Management
Green IoT solar also facilitates optimized energy management by providing granular insights into energy consumption patterns and grid interactions. By integrating IoT-enabled smart meters, energy storage systems, and home automation devices, solar energy users can better manage their energy usage, store excess energy for later use, and even participate in grid-balancing initiatives such as demand response programs.
Enhanced Environmental Sustainability
The integration of IoT technology with solar energy systems contributes to enhanced environmental sustainability by maximizing the efficiency of renewable energy generation. By optimizing solar energy production and consumption, green IoT solar reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowers carbon emissions, and helps mitigate the impacts of climate change. Additionally, by enabling smarter energy management and grid integration, green IoT solar supports the transition to a more decentralized, resilient, and sustainable energy infrastructure.
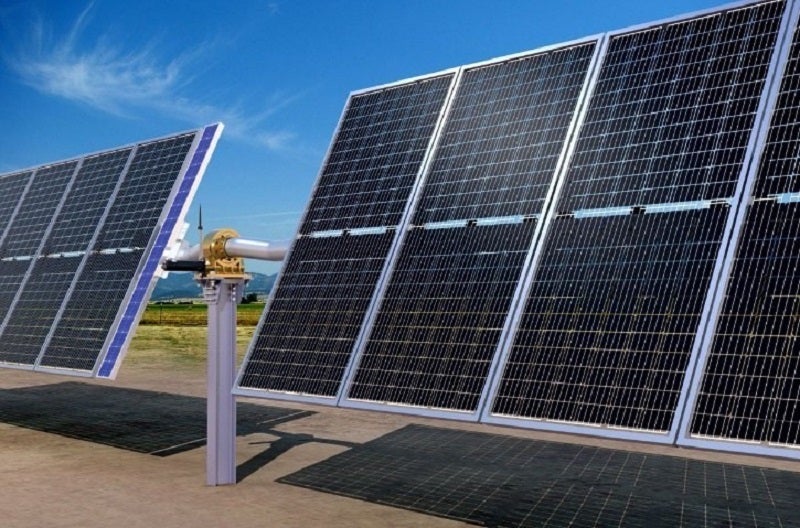
Scalable and Modular Solutions
Another advantage of green IoT solar is its scalability and modularity, allowing for flexible deployment in a variety of settings. Whether it’s a small residential solar installation or a large-scale commercial solar farm, IoT-enabled solar energy systems can be tailored to meet specific needs and scale up or down as required. This flexibility makes green IoT solar an attractive option for a wide range of applications, from individual homes