Understanding the Urgency of Ransomware Protection Ransomware continues to pose a severe threat to individuals and organizations, making robust protection…
Read More

Understanding the Urgency of Ransomware Protection Ransomware continues to pose a severe threat to individuals and organizations, making robust protection…
Read More
Security Tokens: Enhancing Investment Safety and Accessibility In the dynamic landscape of finance, security tokens have emerged as a transformative…
Read More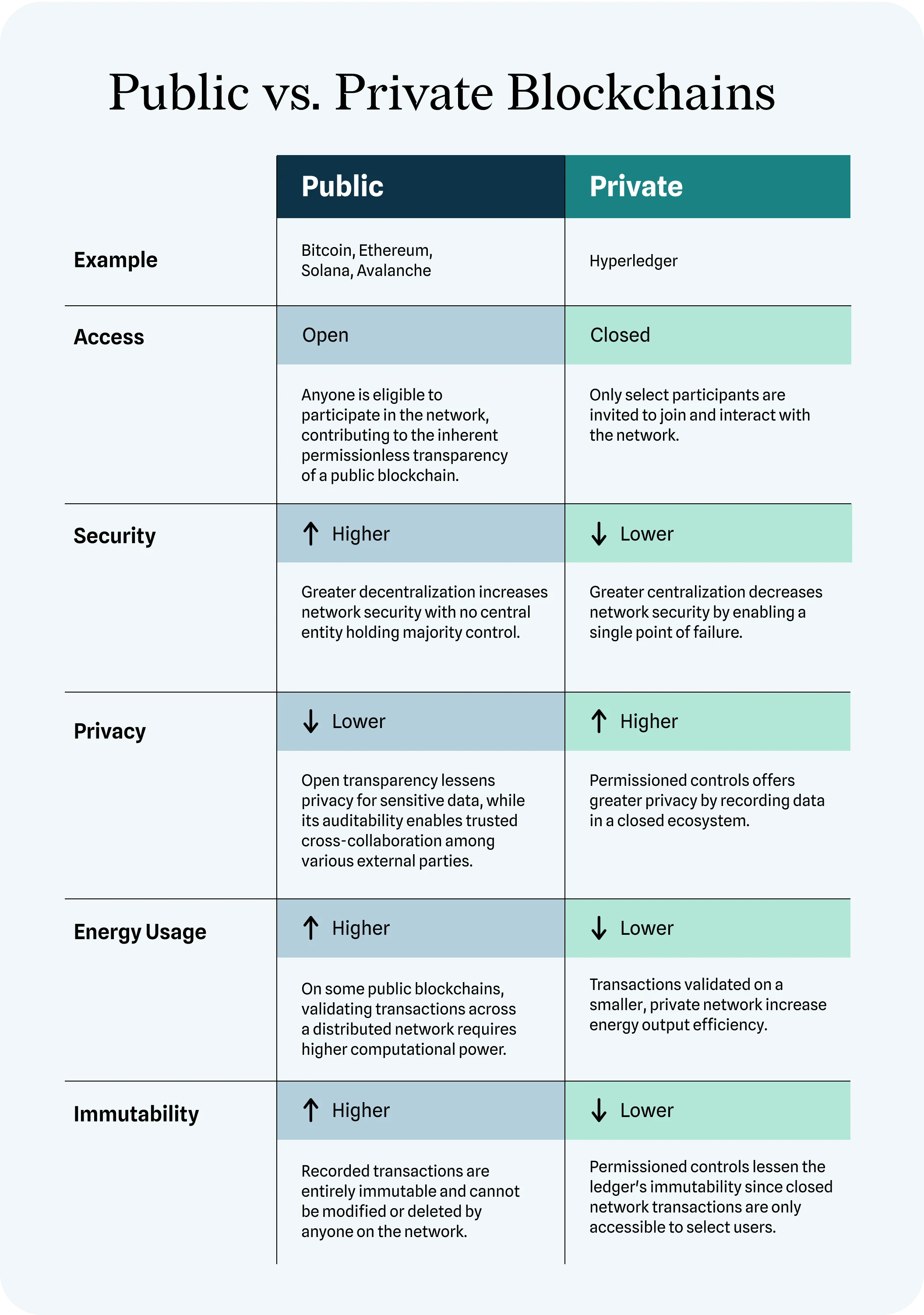
Navigating Digital Ledger Dynamics: Public and Private Blockchains In the vast landscape of blockchain technology, two prominent variants, public and…
Read More
Fortifying Transactions: Secure Enclave Blockchain Blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries with its decentralized and secure nature. The integration of…
Read More
Revolutionizing Art Investments: The Promise of Tokenized Security The world of art, traditionally characterized by exclusivity and high barriers to…
Read More
Understanding the Imperative of Malware Resistance Malware resistance is a critical facet of cybersecurity, representing the collective efforts to fortify…
Read More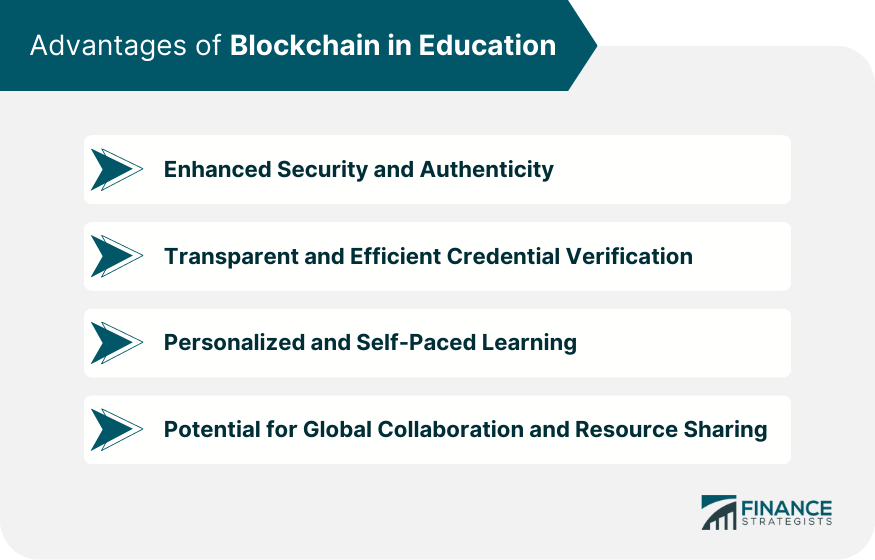
Revolutionizing Academic Verification: Secure Tokenized Education Credentials In the fast-paced digital age, traditional methods of verifying education credentials face challenges…
Read More

Exploring Trustworthy Transactions: Secure Borrowing on the Blockchain Decentralized finance (DeFi) has revolutionized traditional lending and borrowing systems by leveraging…
Read More
Unlocking the Potential: Demystifying Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in Blockchain In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, consensus mechanisms play a pivotal…
Read More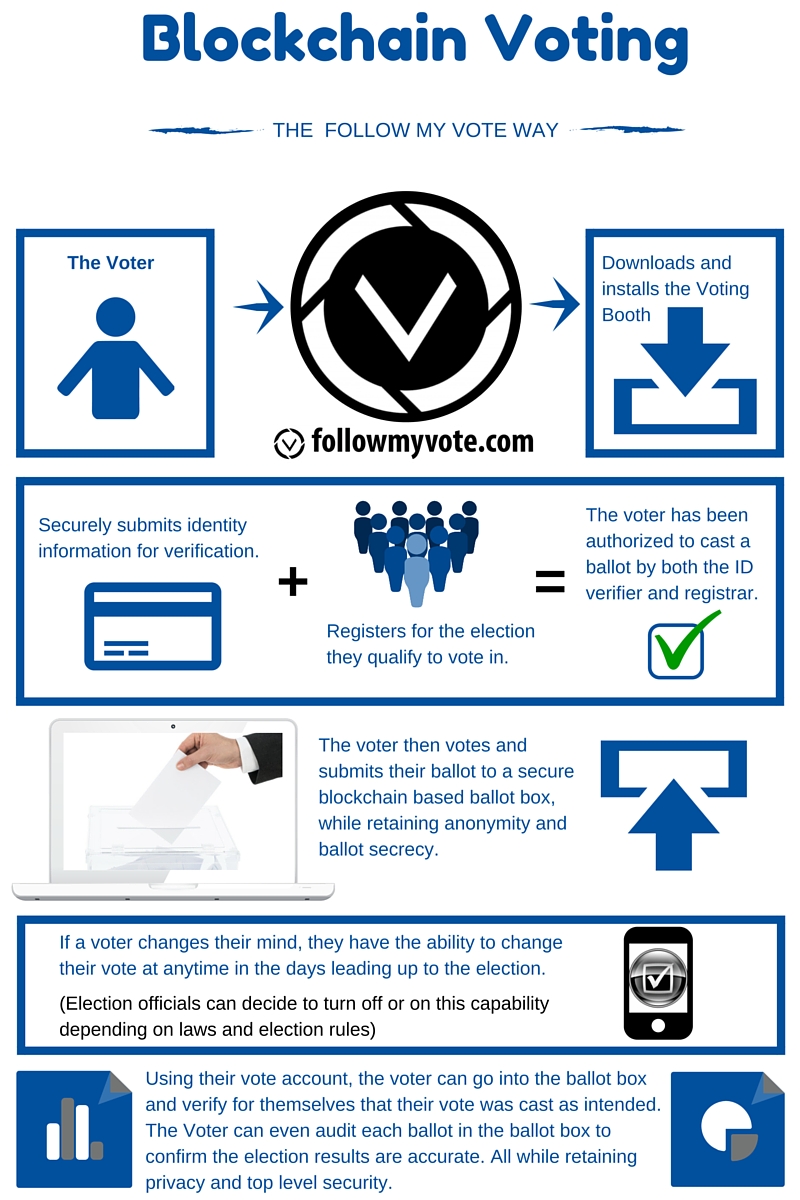
Advancing Electoral Integrity with Secure Blockchain Voting Blockchain technology is increasingly being explored as a solution to enhance the security…
Read More
Blockchain Ballots: Reinventing Voting with Security Blockchain technology is reshaping traditional voting systems, introducing a new era of secure and…
Read More
Securing Returns in Decentralized Finance through Yield Farming Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has revolutionized traditional financial systems, offering users the opportunity…
Read More
Ensuring AML Compliance: Safeguarding Financial Integrity Anti-money laundering (AML) compliance is a critical aspect of the financial industry, playing a…
Read More
Exploring Byzantine Fault Tolerance: Navigating Reliability in Blockchain In the intricate landscape of blockchain technology, Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) stands…
Read More
Transforming IP Protection: The Era of Tokenized Security The landscape of intellectual property (IP) protection is experiencing a revolutionary shift…
Read More
Privacy Coins: Securing Transactions on the Blockchain Privacy coins have emerged as a significant innovation within the blockchain space, offering…
Read More
Interwoven Chains: Safeguarding Transactions with Cross-Chain Security Cross-chain security has become a pivotal consideration in the ever-expanding blockchain landscape. In…
Read More
Tokenization: Transforming Assets into Digital Value The concept of tokenization is revolutionizing the way we perceive and handle various forms…
Read More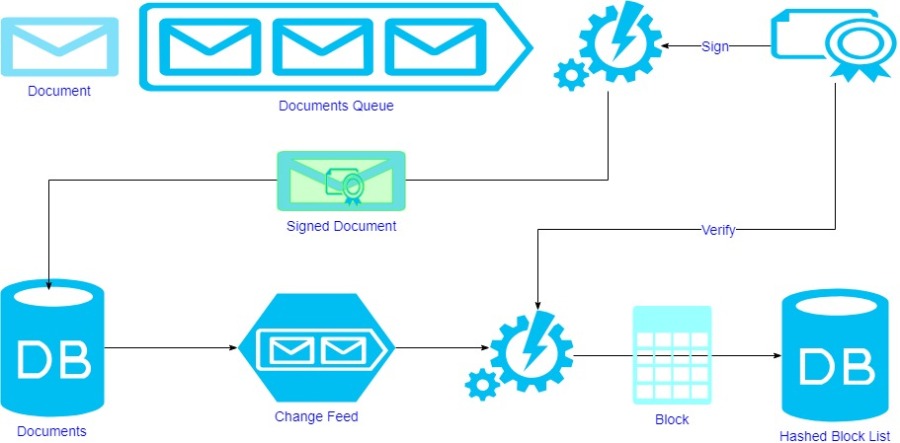
Ensuring Unalterable Data Integrity with Immutable Audit Trails In the realm of data management, the concept of immutable audit trails…
Read More
Decoding the Intricacies of Blockchain Mining Blockchain technology has undoubtedly been a revolutionary force, transforming industries and reshaping how we…
Read More
You may be puzzled by the many features of an iphone if you have only recently purchased one. Do not…
Read More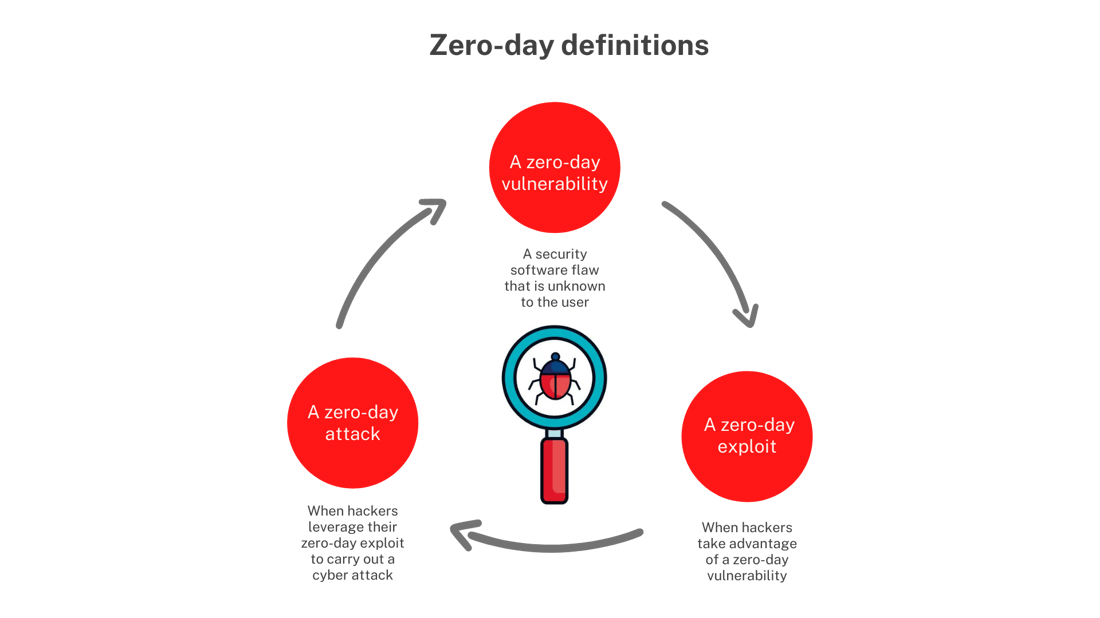
Unveiling Zero-Day Threats: Cybersecurity Challenges In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerabilities pose significant challenges for organizations striving to…
Read More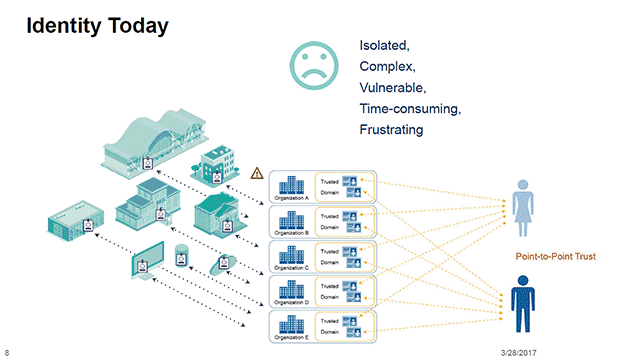
Blockchain-Powered Identity Management for Enhanced Security Identity management is undergoing a revolutionary transformation through the integration of blockchain technology. This…
Read MoreSecuring Energy Trading: Blockchain’s Transparent Innovation Energy trading is undergoing a significant transformation with the integration of blockchain technology. This…
Read More
Fortifying Trade Finance: Secure Tokenized Solutions for Trust In the intricate web of global trade, the security and efficiency of…
Read More
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital assets, Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a revolutionary form of ownership and representation.…
Read More
NIST Guidelines: Shaping Digital Standards for Cybersecurity The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) stands as a linchpin in…
Read More
Enhancing Security: The Power of Secure Hardware Modules Security is a paramount concern in the digital age, and advancements in…
Read More
Revolutionizing Democracy: The Security of Tokenized Voting Contracts In the realm of democratic processes, the integration of secure tokenized voting…
Read More
The Unchanging Foundation: Exploring the Immutable Ledger In the realm of digital transactions and record-keeping, the concept of an immutable…
Read More
Hot Wallets: Convenient Access for Digital Asset Management The world of cryptocurrency presents various storage options, and hot wallets stand…
Read More

Navigating the Landscape: Blockchain Interoperability Standards The blockchain ecosystem, with its decentralized and distributed nature, has revolutionized various industries. However,…
Read More
Blockchain Fortification: Unveiling the Significance of Security Standards Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized and tamper-resistant nature, relies on robust…
Read More
Revolutionizing Real Estate Transactions: The Security of Tokenized Contracts In the ever-evolving real estate industry, the integration of secure tokenized…
Read More
Revolutionizing Creative Ventures: The Security of Tokenized Royalty Contracts In the realm of creative industries, the introduction of secure tokenized…
Read More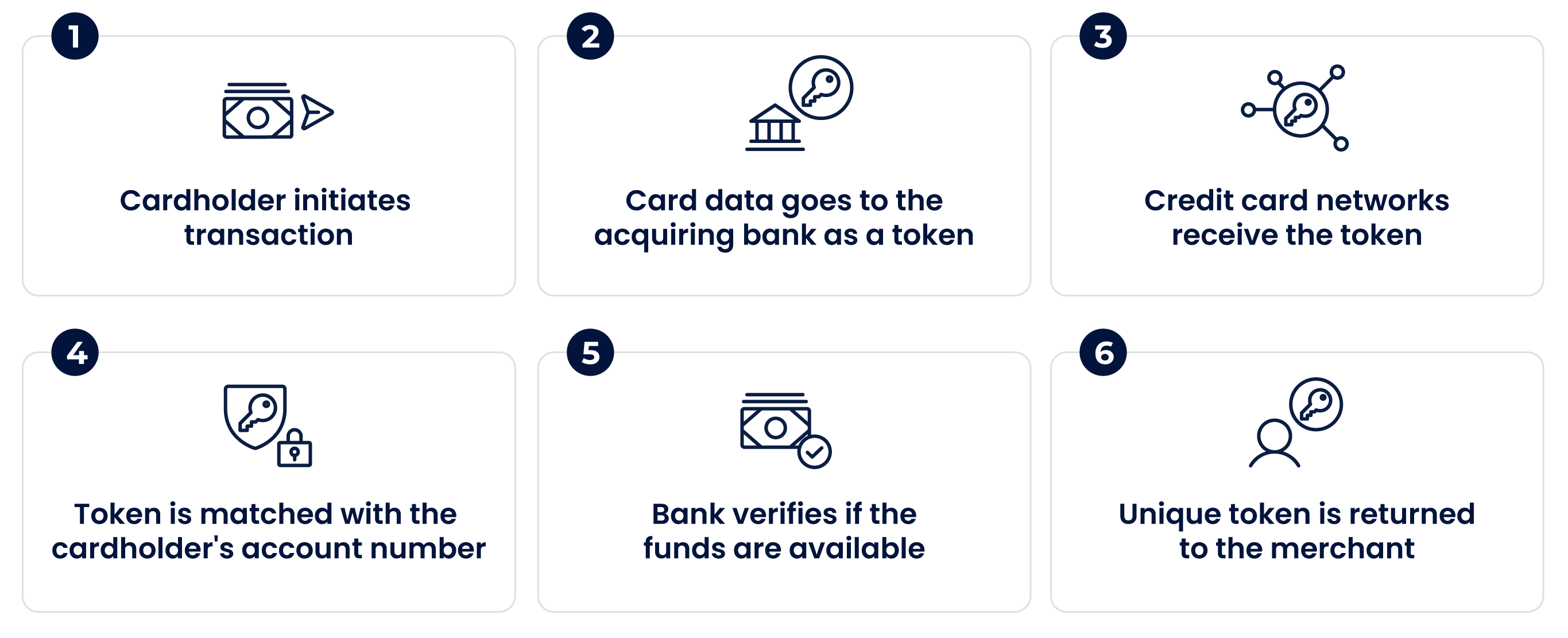
Transforming Legal Transactions: The Security of Tokenized Documents In the era of digitization, legal documents play a crucial role in…
Read More
Revolutionizing Athletic Agreements: The Security of Tokenized Sports Contracts In the ever-evolving world of sports, the introduction of secure tokenized…
Read More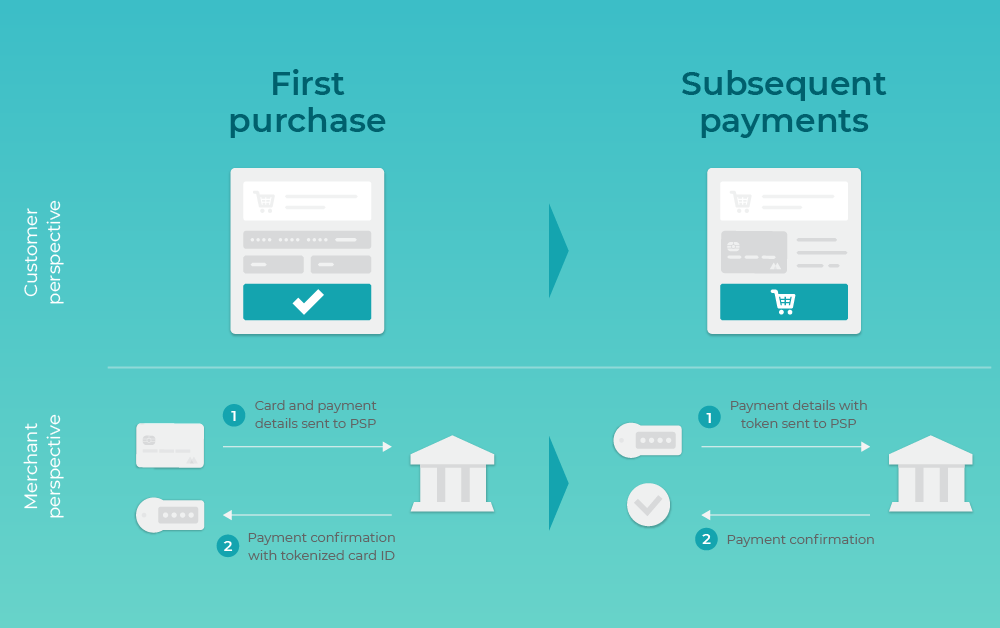
Securing Supply Chains: Tokenized Finance for Trustworthy Operations In the intricate world of supply chains, financial transactions play a critical…
Read MoreUnlocking Privacy: The Power of Secure Multi-Party Computation In the realm of digital privacy and secure data collaboration, Secure Multi-Party…
Read More
Fortify Security with Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) In an era where digital threats loom large, safeguarding your online accounts and sensitive…
Read More
Navigating Blockchain: The Crucial Role of Governance Blockchain governance is a fundamental aspect that influences the development, security, and sustainability…
Read More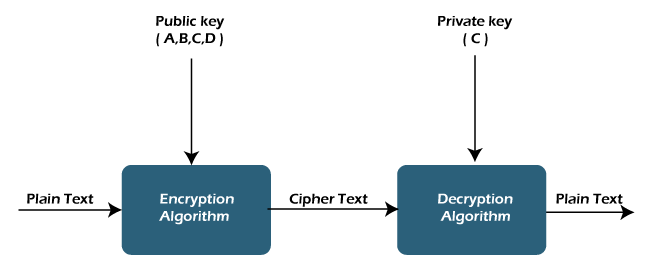
Key Encryption: Safeguarding Data with Public and Private Keys Public and private key encryption is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity,…
Read More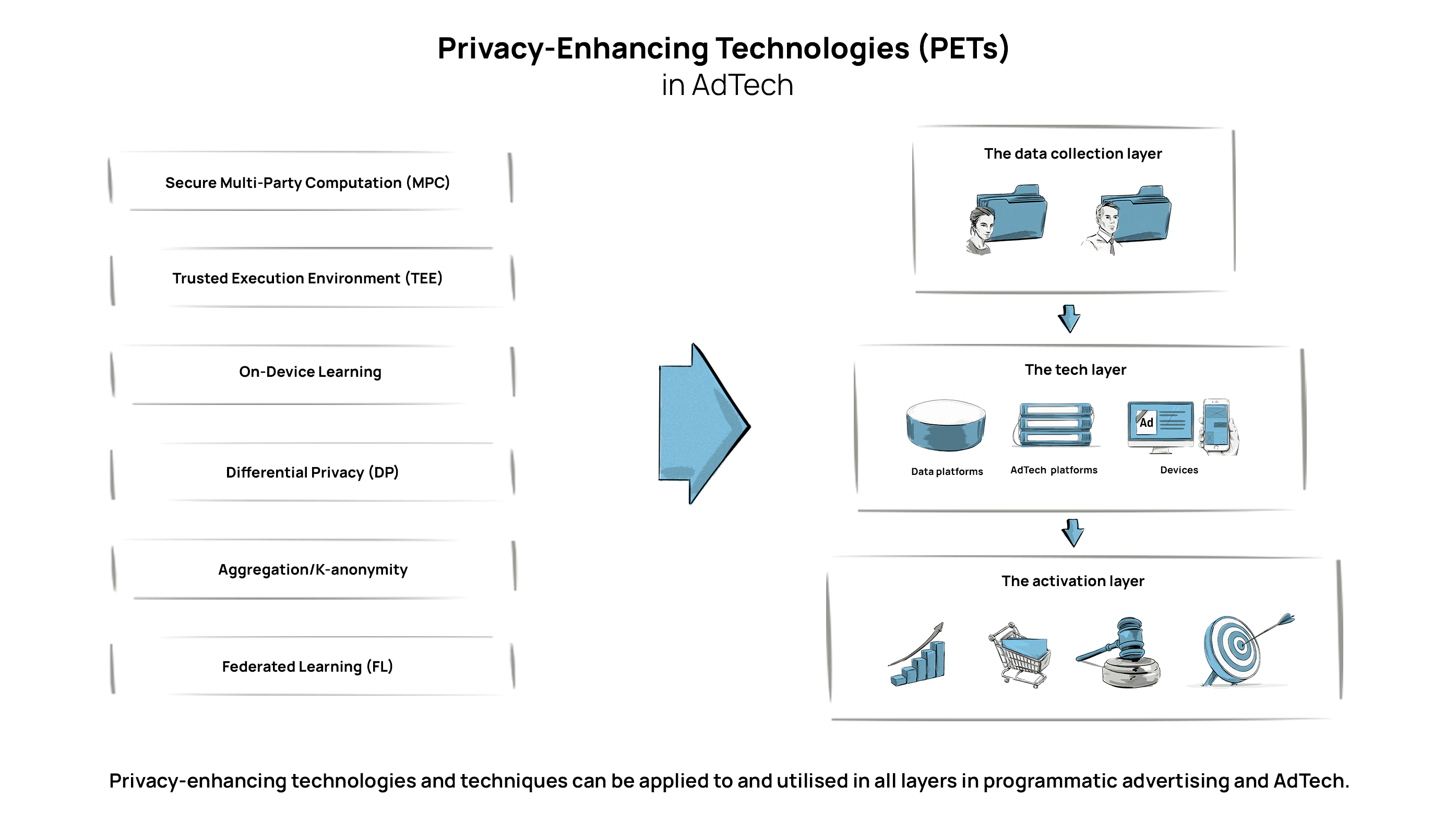
Elevating Privacy: Unveiling the Power of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) emerge as powerful tools in safeguarding individual privacy…
Read More
DeFi Security: Safeguarding the Decentralized Financial Landscape Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has garnered immense popularity for its innovative approach to financial…
Read More
Ensuring Security: Token Standards like ERC-20, ERC-721 Token standards, such as ERC-20 and ERC-721, have become integral components of blockchain…
Read More
Bridging Smart Contracts to Real-World Data: Unveiling Chainlink (LINK) In the realm of blockchain and smart contracts, Chainlink (LINK) has…
Read More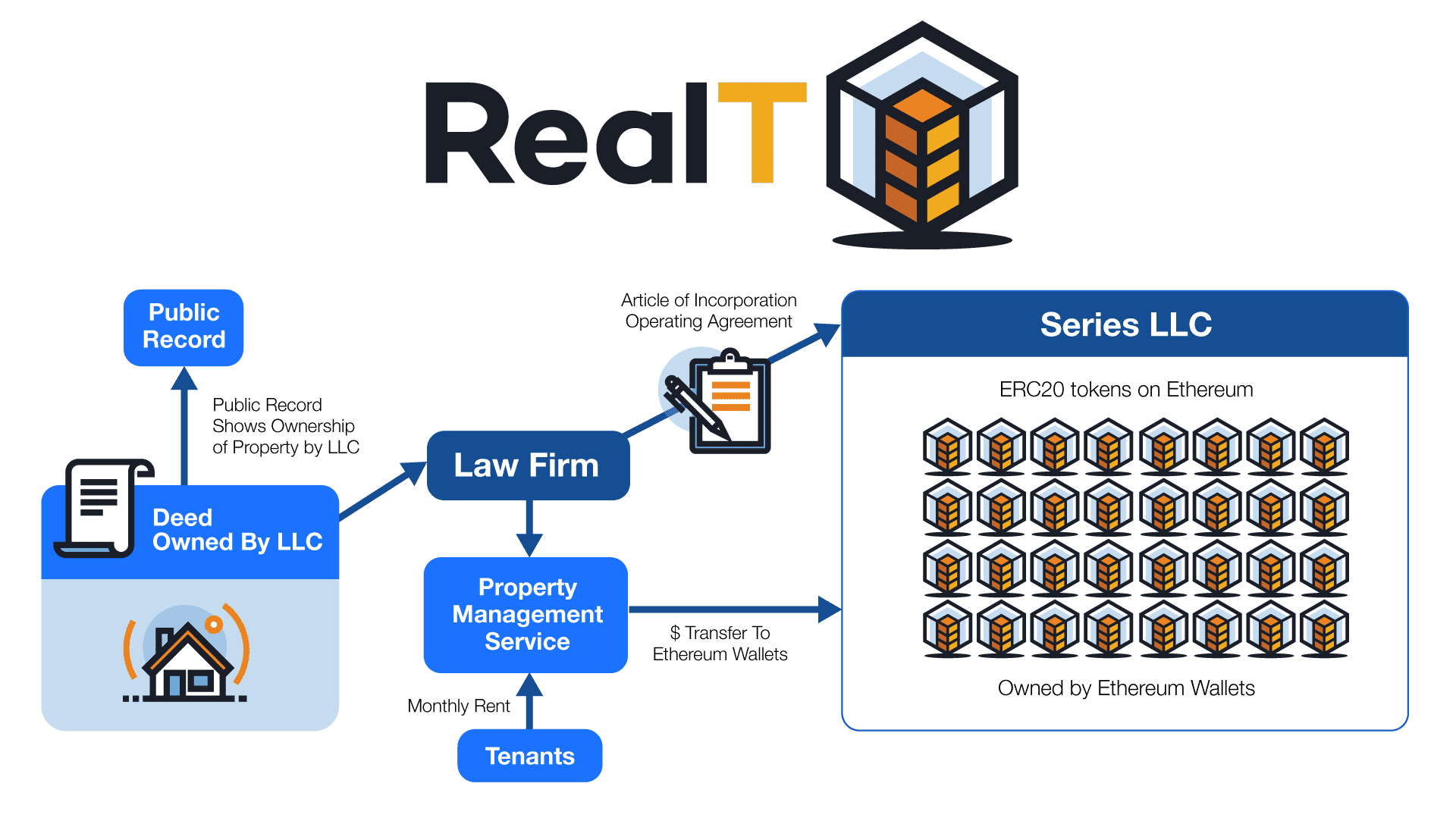
Revolutionizing Innovation: The Security of Tokenized Intellectual Property In the ever-evolving landscape of intellectual property (IP) management, the concept of…
Read More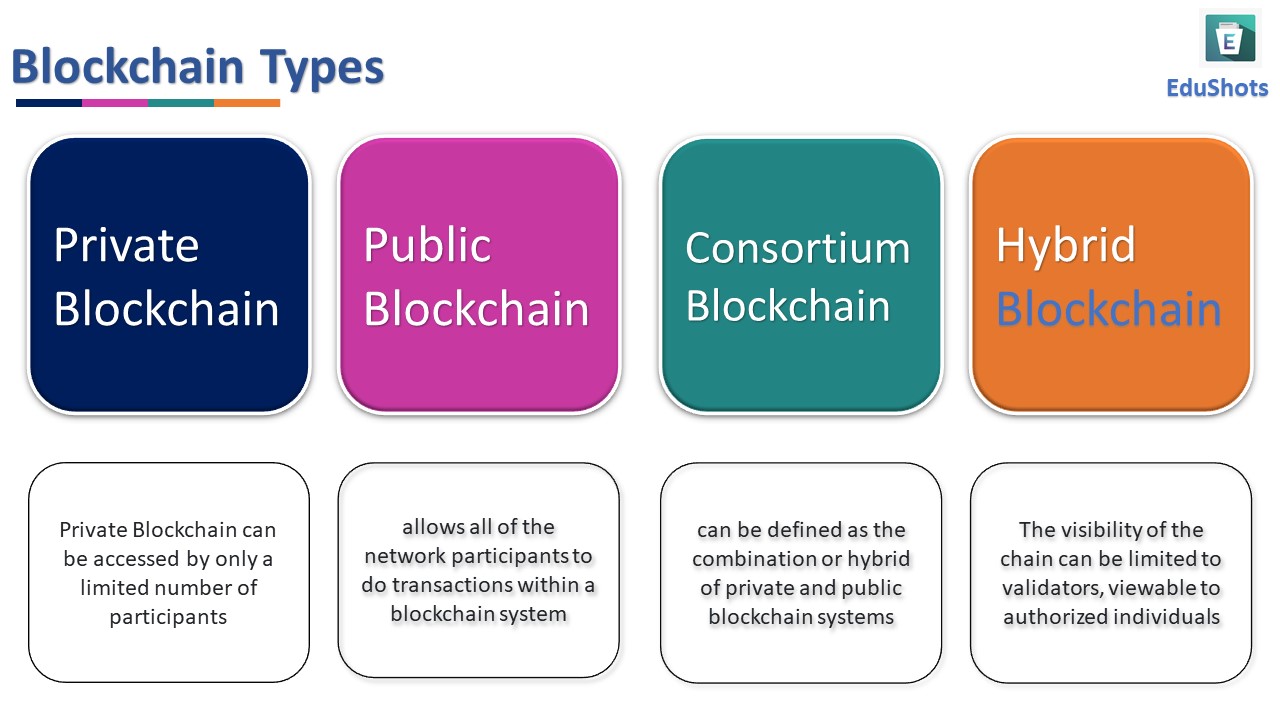
Empowering Collaboration: Essentials of Consortium Blockchains Consortium blockchains, a hybrid between public and private blockchains, offer a middle ground for…
Read More