Key Encryption: Safeguarding Data with Public and Private Keys
Public and private key encryption is a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity, providing a robust method for securing sensitive data. This article delves into the principles behind this encryption technique, its applications, and why it is crucial in safeguarding digital information.
Understanding Public and Private Key Encryption
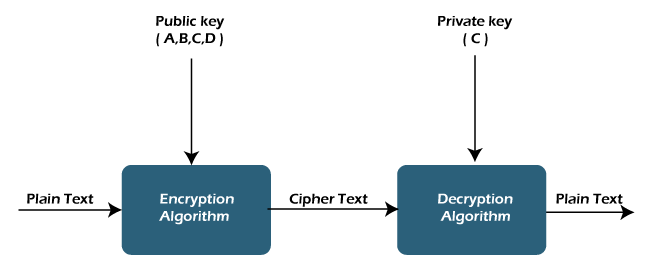
Public and private key encryption, also known as asymmetric encryption, involves the use of a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is shared openly, while the private key is kept secret. Information encrypted with one key can only be decrypted with the corresponding key, adding a layer of security to data transmissions.
The Role of Public Keys: Secure Data Transmission
Public keys serve as a means to securely transmit information. When someone wants to send sensitive data, they use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the information. Only the recipient, who possesses the corresponding private key, can decrypt and access the original data. This process ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the transmitted information.
Private Keys: Uniquely Tied to Individuals
Private keys, on the other hand, are closely guarded by their respective owners. They are used to decrypt data that has been encrypted with the corresponding public key. Since the private key is kept secret, it adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the decrypted information.
Applications in Secure Communication
Public and private key encryption is widely used in secure communication channels, such as HTTPS for secure website connections. When you visit a secure website, your browser and the server exchange public keys to establish a secure connection. This encryption method protects sensitive information, such as login credentials and financial transactions, from eavesdroppers.
Digital Signatures: Verifying Authenticity
Another crucial application of public and private key encryption is in digital signatures. Individuals or entities can use their private key to sign a digital document or message. The recipient can then verify the authenticity of the signature using the sender’s public key, ensuring that the content has not been altered and originates from the claimed source.
Blockchain Technology: Immutable Transactions
Public and private key encryption plays a pivotal role in blockchain technology. Each participant in a blockchain network has a unique public and private key pair. Transactions are securely signed with the private key, and the integrity of the transaction is verified by others using the sender’s public key. This process ensures the immutability and security of transactions on the blockchain.
Challenges and Considerations
While public and private key encryption is highly secure, it is not without challenges. Key management, including secure storage and distribution of keys, is critical. Additionally, the potential risk of private key compromise emphasizes the importance of robust cybersecurity practices to protect sensitive cryptographic keys.
Future Developments in Key Encryption
As technology evolves, advancements in quantum computing pose potential threats to traditional encryption methods. Post-quantum cryptography research is underway to develop algorithms resistant to quantum attacks. The future