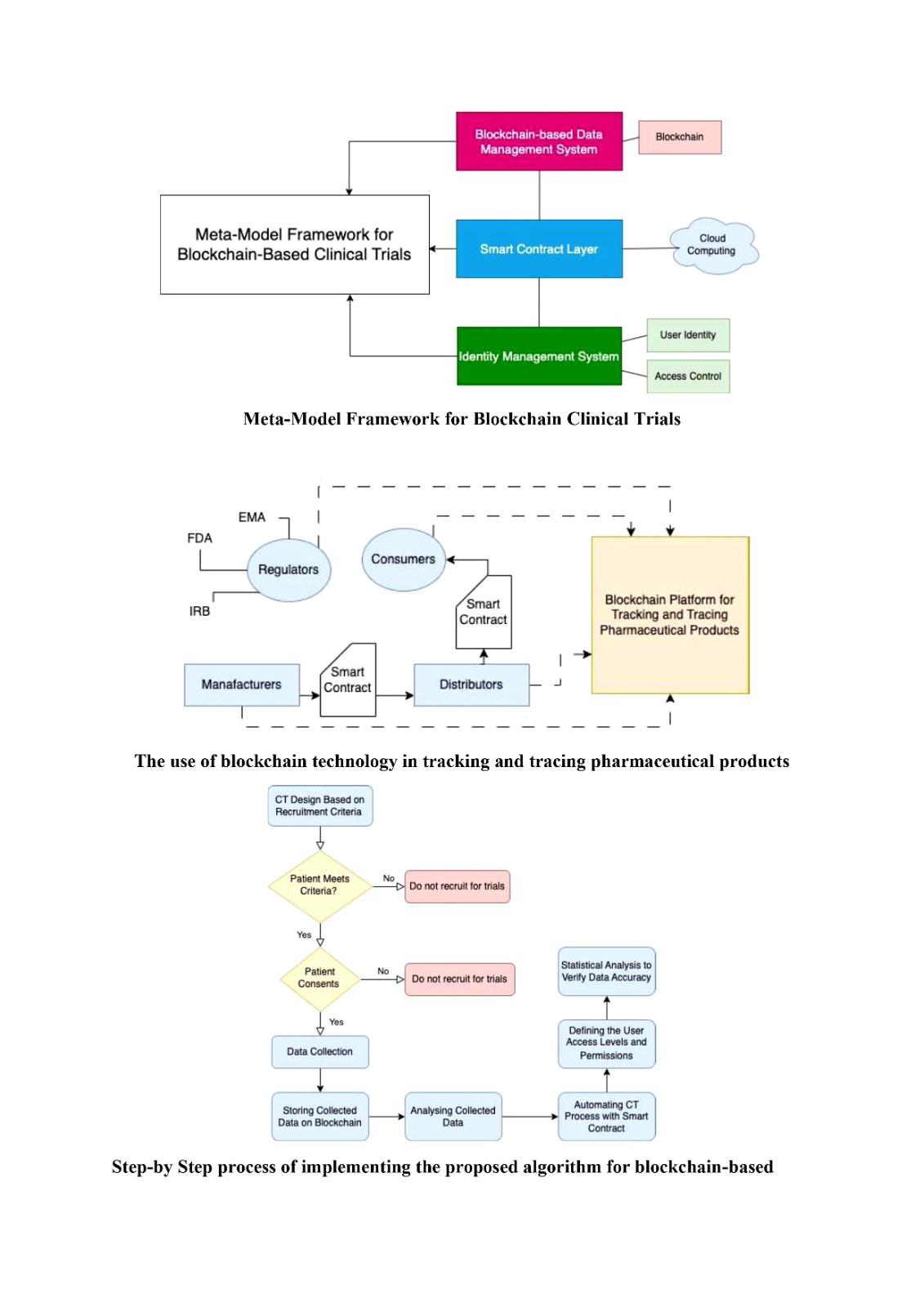
CryptoVault: Elevating Data Storage Security with Blockchain
In the digital age, the security of data storage is paramount, and the integration of blockchain technology introduces CryptoVault, a revolutionary solution designed to fortify and secure data storage. This article explores the significance and transformative impact of secure data storage on the blockchain.
The Significance of Secure Data Storage
As organizations grapple with the increasing volumes of sensitive data, the significance of secure data storage cannot be overstated. Traditional storage methods often face vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, data tampering, and single points of failure. CryptoVault, powered by blockchain, addresses these challenges by providing a decentralized and tamper-resistant solution.
Blockchain’s Decentralization and Tamper-Resistance
The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that data is not stored in a single central location, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or manipulation. Each data transaction is recorded in a block, linked to the previous one, creating an immutable chain of information. This tamper-resistant feature establishes a robust defense against data breaches and unauthorized alterations.
Smart Contracts Automating Data Storage Protocols
CryptoVault leverages smart contracts, self-executing programs on the blockchain, to automate data storage protocols. These contracts define the rules and conditions under which data transactions are stored, providing a secure and efficient way to manage data. The automated execution of these protocols reduces the reliance on centralized control, minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing overall security.
Enhanced Security Through Blockchain Consensus
Blockchain’s consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, contribute to enhanced security in data storage. Before a data transaction is added to the blockchain, consensus among network participants is required. This distributed agreement ensures that only valid and authorized data transactions are recorded, adding an extra layer of security against malicious activities.
Transparent and Auditable Data Transactions
Secure data storage on the blockchain ensures transparency and auditability of data transactions. Every interaction with the data, from creation to modification, is recorded on the blockchain. This transparency not only provides a real-time view of data activities but also establishes an auditable trail. Organizations can easily track and verify the history of data transactions for compliance and accountability purposes.
Immutable Records for Data Integrity
CryptoVault’s use of blockchain ensures the immutability of data records. Once data is stored on the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unchangeable part of the ledger. This feature safeguards the integrity of data, preventing unauthorized modifications and establishing a reliable record of the information’s history.
Data Encryption Measures for Privacy Protection
Privacy is a critical consideration in data storage, and CryptoVault addresses this by incorporating robust data encryption measures. While blockchain provides transparency, encryption ensures that certain details are accessible only to authorized parties. This careful balance between transparency and privacy protection ensures that sensitive data remains confidential and secure.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing CryptoVault
Implementing CryptoVault for secure data storage is not without challenges. Issues such as scalability, interoperability, and integration with existing systems need careful consideration. Ongoing collaboration within the industry and technological advancements