Securing Consensus Participants for Robust Blockchain Systems
Blockchain systems rely on a decentralized consensus mechanism to validate and agree upon transactions. Ensuring the security of consensus participants is paramount for the overall robustness and trustworthiness of the blockchain network.
The Significance of Consensus Participants in Blockchain
Consensus participants are nodes or entities within a blockchain network responsible for validating and confirming the legitimacy of transactions. These participants play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and security of the entire system. Securing them is vital to prevent malicious activities that could compromise the trust in the blockchain.
Decentralization and Security
Decentralization is a key principle of blockchain technology, distributing the validation process across multiple participants. However, this decentralization introduces new challenges in terms of security. Each consensus participant must be protected to safeguard against attacks that could disrupt the functioning of the network.
Cryptography for Participant Authentication
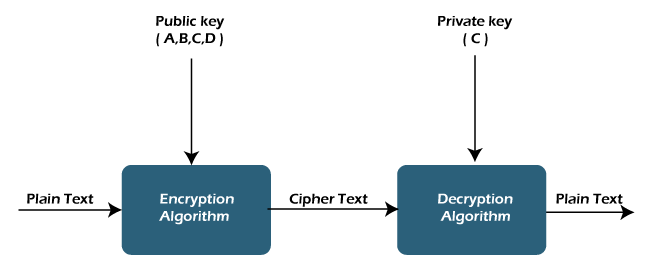
Implementing robust cryptographic techniques is essential for authenticating consensus participants. Public-key cryptography, for example, enables secure communication and ensures that each participant is uniquely identified. This authentication layer adds an extra level of security, preventing unauthorized entities from participating in the consensus process.
Secure Communication Channels
Creating secure communication channels between consensus participants is vital for preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Utilizing encryption protocols ensures that the information exchanged during the consensus process remains confidential and tamper-resistant. This secure communication is fundamental to the overall security of the blockchain system.
Participant Access Control and Authorization
Implementing strict access control mechanisms is crucial to managing the permissions of consensus participants. Only authorized entities should be allowed to participate in the consensus process. By enforcing access control policies, blockchain networks can mitigate the risk of malicious actors attempting to manipulate the consensus mechanism.
Continuous Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Real-time monitoring of consensus participants is essential to detect any suspicious activities promptly. Intrusion detection systems can identify unusual behavior or unauthorized access attempts, triggering immediate responses to mitigate potential threats. This proactive approach enhances the overall security posture of the blockchain network.
Diversity in Consensus Mechanisms
Diversifying consensus mechanisms can contribute to the security of blockchain networks. Depending on the use case, different consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) can be employed. This diversity makes it more challenging for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities across various types of consensus participants.
Regular Security Audits and Updates
To adapt to evolving security threats, regular security audits and updates are essential. Consensus participants’ software and configurations should be regularly reviewed and updated to patch vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with the latest security best practices. This ongoing maintenance is crucial for a resilient blockchain infrastructure.
Community Education and Best Practices
Educating consensus participants and the broader blockchain community on security best practices is integral to maintaining a secure network. Providing guidelines, resources, and training helps participants understand their role in the security ecosystem and encourages a collective commitment to maintaining a robust blockchain infrastructure.
The Future of Secure Consensus