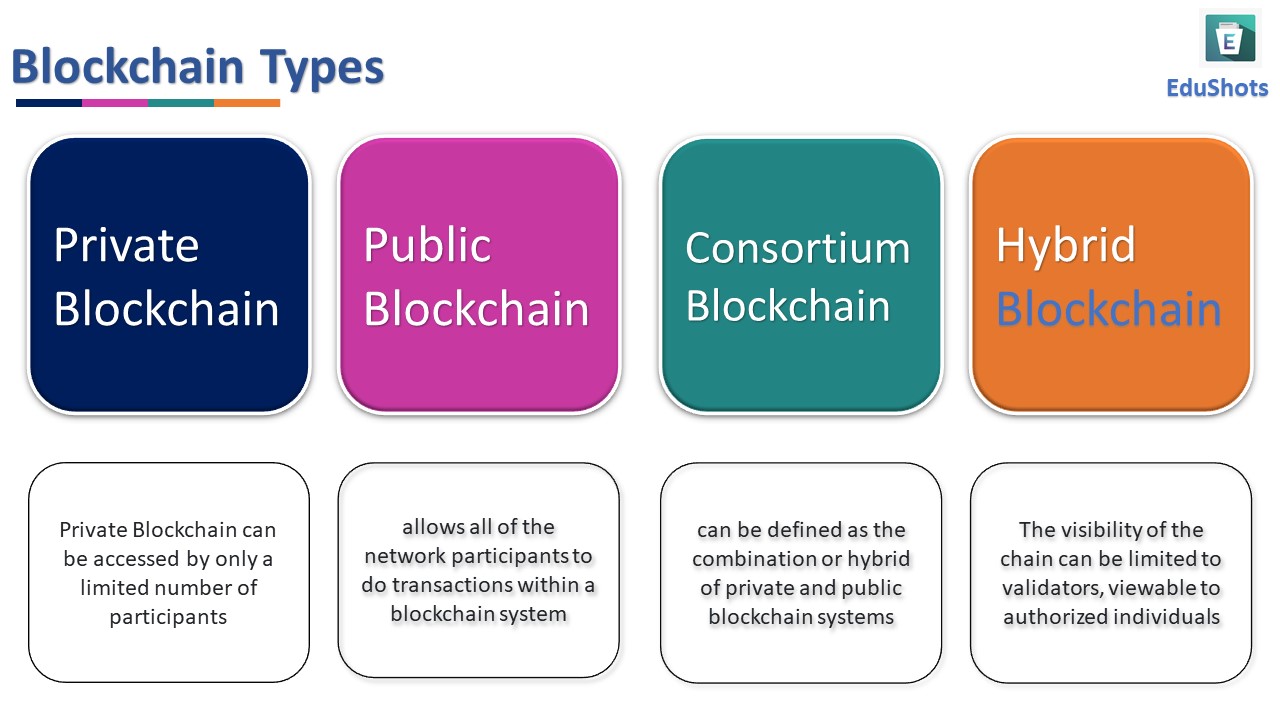
Blockchain Fortification: Unveiling the Significance of Security Standards
Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized and tamper-resistant nature, relies on robust security standards to maintain integrity. This article delves into the pivotal role of security standards in blockchain, exploring their importance, key components, and the collaborative efforts shaping a secure blockchain landscape.
The Crucial Role of Security Standards in Blockchain
1. Upholding Trust in Decentralization
Security standards serve as the backbone of trust in blockchain systems. In a decentralized environment, where multiple participants contribute to the network, adhering to stringent security standards ensures that data integrity and confidentiality are preserved. These standards create a foundation of trust, essential for widespread adoption.
2. Mitigating Risks and Vulnerabilities*
Blockchain security standards are designed to mitigate risks and vulnerabilities inherent in decentralized networks. By establishing guidelines for secure coding practices, data encryption, and access controls, these standards significantly reduce the potential for malicious exploits, ensuring a more resilient blockchain ecosystem.
Key Components of Blockchain Security Standards
1. Consensus Algorithm Integrity*
Security standards address the integrity of consensus algorithms, the mechanisms that ensure agreement among nodes in a blockchain network. By establishing protocols for consensus algorithm implementation, standards contribute to the overall security and reliability of the blockchain’s agreement process.
2. Smart Contract Security Guidelines*
Smart contracts, self-executing code snippets integral to many blockchain applications, are subject to security standards. These guidelines focus on secure coding practices, emphasizing the importance of thorough testing and auditing to identify and rectify vulnerabilities within smart contracts.
3. Data Encryption Protocols*
Security standards mandate robust data encryption protocols to safeguard information stored on the blockchain. Encryption ensures that sensitive data remains confidential, even in a transparent and decentralized ledger, adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Collaborative Efforts in Shaping Blockchain Security Standards
1. Industry Collaboration and Best Practices*
The development of security standards in blockchain is a collaborative effort involving industry experts, developers, and regulatory bodies. By sharing insights, experiences, and best practices, the blockchain community contributes to the evolution of security standards that address emerging threats and challenges.
2. Regulatory Compliance and Standardization*
As blockchain gains prominence, regulatory bodies worldwide are actively working on standardizing security measures. Compliance with these regulations becomes crucial for blockchain projects, providing a framework that aligns with broader cybersecurity principles and legal requirements.
Challenges and Evolving Trends in Blockchain Security Standards
1. Adaptation to Technological Advances*
The rapid evolution of blockchain technology poses challenges for security standards. As blockchain platforms and applications advance, standards must adapt to new features, consensus mechanisms, and cryptographic protocols to ensure continued effectiveness in mitigating emerging threats.
2. Addressing Privacy Concerns*
The integration of privacy features in blockchain, such as zero-knowledge proofs and privacy coins, introduces complexities for security standards. Balancing the transparency of the ledger with the need for privacy requires ongoing efforts in refining security standards to address these intricacies.
Empowering Blockchain Security with Standards Resources
For a deeper exploration of security standards in blockchain