Sub Heading: Deciphering the Economics: Hydrogen Plant Cost
Hydrogen plant cost is a pivotal factor in the development and implementation of hydrogen production facilities, influencing their feasibility and economic viability. Understanding the various components and factors that contribute to hydrogen plant costs is essential for stakeholders and investors looking to capitalize on the growing demand for hydrogen as a clean energy source.
Sub Heading: Initial Investment and Capital Expenditure
The initial investment required to establish a hydrogen production plant encompasses a range of capital expenditures, including land acquisition, infrastructure development, and equipment procurement. Factors such as site location, plant capacity, and technology selection can significantly impact the upfront costs associated with building a hydrogen plant. Additionally, regulatory compliance, permitting, and licensing requirements may add further expenses to the initial investment phase.
Sub Heading: Technology Selection and Process Efficiency
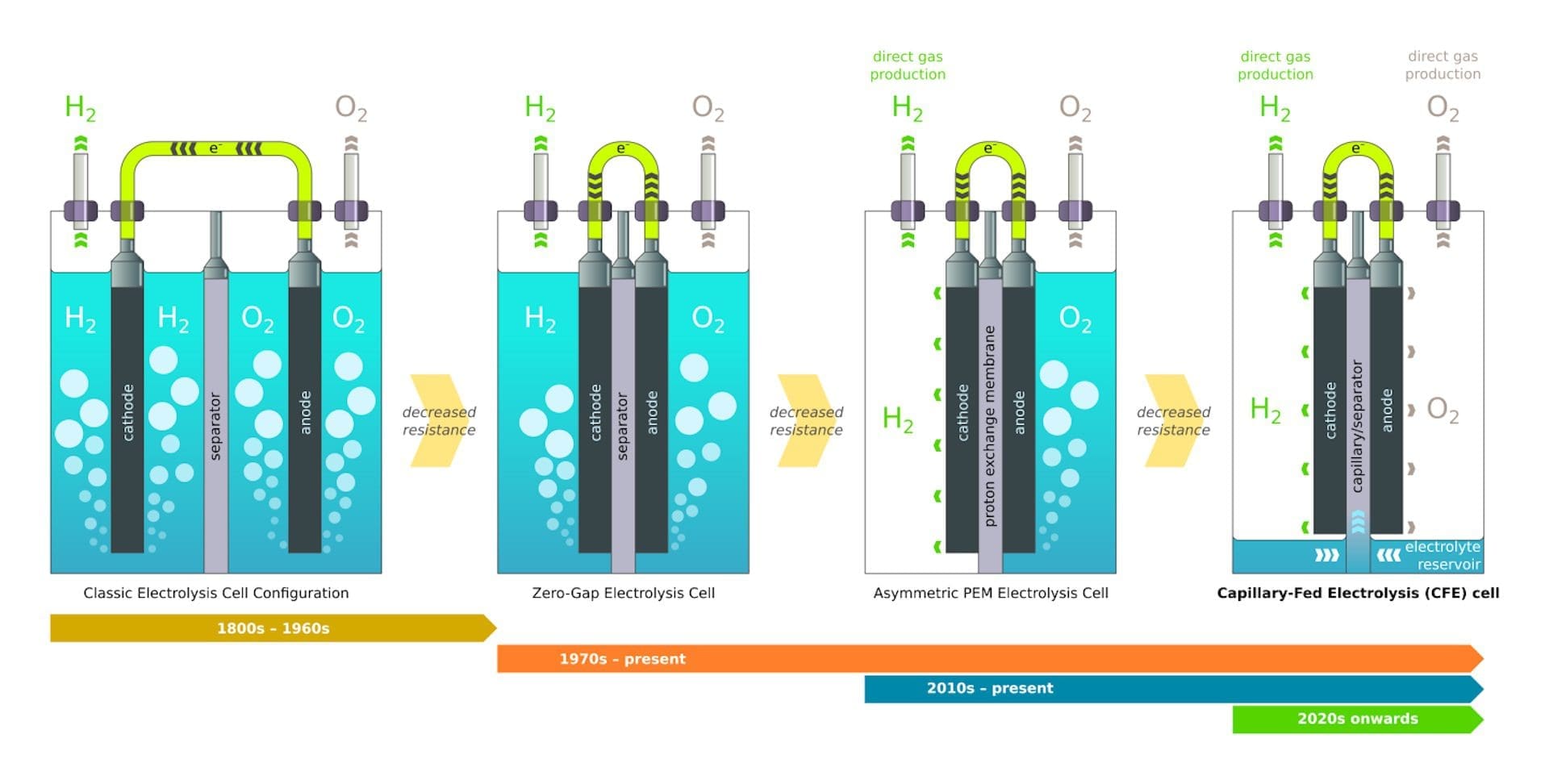
The choice of technology and production process employed in a hydrogen plant can have a significant impact on its overall cost structure and operational efficiency. Different technologies, such as steam methane reforming (SMR), electrolysis, and biomass gasification, have varying capital and operational costs, as well as different levels of efficiency and environmental impact. Selecting the most suitable technology for a hydrogen plant requires careful consideration of factors such as feedstock availability, energy prices, and emissions reduction goals.
Sub Heading: Feedstock Procurement and Supply Chain Management
Feedstock procurement plays a crucial role in determining the cost competitiveness and sustainability of hydrogen production. The availability and cost of feedstocks such as natural gas, water, and biomass can vary depending on factors such as geographical location, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks. Effective supply chain management and strategic partnerships with suppliers are essential for ensuring reliable and cost-effective feedstock procurement, minimizing production costs, and optimizing plant operations.
Sub Heading: Energy Consumption and Operating Expenses
Energy consumption is a major cost driver in hydrogen production, particularly in processes such as steam methane reforming and electrolysis that require significant amounts of electricity or heat. Optimizing energy efficiency through process improvements, equipment upgrades, and the integration of renewable energy sources can help reduce operating expenses and enhance the economic competitiveness of hydrogen plants. Additionally, ongoing maintenance, labor, and utility costs contribute to the overall operating expenses of hydrogen production facilities.
Sub Heading: Scale and Production Volume
The scale of a hydrogen plant and its production volume have a direct impact on its cost structure and economies of scale. Larger-scale facilities generally benefit from lower unit costs due to higher production volumes, reduced overhead expenses, and economies of scale in equipment procurement and operations. However, scaling up hydrogen production capacity also entails higher initial investment and infrastructure costs, requiring careful assessment of market demand and growth projections.
Sub Heading: Regulatory and Policy Considerations
Regulatory frameworks and government policies can significantly influence the cost dynamics and investment incentives associated with hydrogen production. Subsidies, tax incentives, and carbon pricing mechanisms may help offset the capital and operating costs of hydrogen plants, making them more financially attractive to investors. Additionally, supportive policies such