Strengthening Security: The Role of Multi-signature (Multisig) in Digital Transactions
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital transactions, security remains a paramount concern. Multi-signature, commonly referred to as multisig, has emerged as a robust solution to enhance security in various digital interactions. Let’s delve into the intricacies of multisig and its pivotal role in safeguarding digital transactions.
Understanding Multi-signature (Multisig)
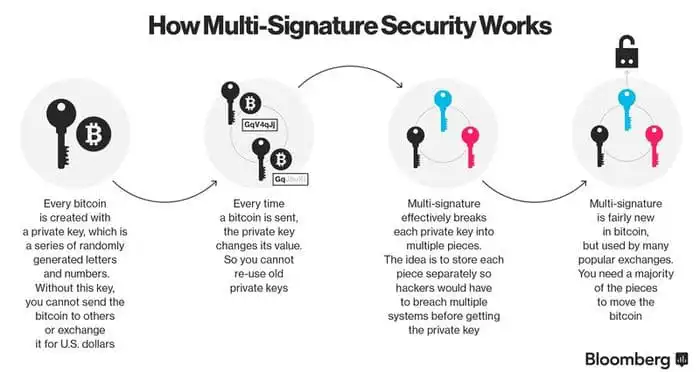
Multisig is a cryptographic technique that involves multiple private keys to authorize a transaction. Unlike traditional single-key transactions, where a single private key is sufficient for validation, multisig requires the collaboration of multiple parties, each possessing a unique private key. This approach adds an extra layer of security by distributing control among multiple entities.
How Multisig Works
In a multisig setup, a predetermined number of private keys out of a total set must collectively authorize a transaction. For example, in a 2-of-3 multisig configuration, any two out of the three private keys are required to validate and execute the transaction. This mechanism prevents a single point of failure and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access.
Applications in Digital Transactions
The versatility of multisig extends across various digital transaction scenarios. It is prominently used in cryptocurrency wallets, where the owner might distribute control among multiple devices or trusted individuals. Businesses can also benefit from multisig by implementing approval processes that involve multiple stakeholders, ensuring secure and authorized transactions.
Enhanced Security in Cryptocurrency Wallets
In the realm of cryptocurrencies, multisig plays a crucial role in securing digital assets. A multisig wallet requires multiple signatures to initiate a transaction, making it significantly more resilient against unauthorized access or hacking attempts. This feature is especially appealing to users who prioritize the security of their cryptocurrency holdings.
Reducing Single Points of Failure
Traditional single-key setups pose a vulnerability where the compromise of a single key grants unauthorized access. Multisig addresses this concern by distributing control, reducing the risk associated with a single point of failure. This makes multisig an attractive option for individuals and organizations aiming to fortify their digital security.
Challenges and Considerations
While multisig enhances security, its implementation introduces complexities. Determining the appropriate number of required signatures and managing the distribution of private keys require careful consideration. Additionally, the loss of access to one or more private keys can lead to complications. Balancing security with usability is an ongoing challenge in the adoption of multisig solutions.
Real-World Implications of Multisig
Consider a business scenario where financial transactions require approval from both the CEO and CFO. A 2-of-2 multisig setup ensures that both key decision-makers must authorize the transaction, adding an extra layer of approval and reducing the risk of fraudulent or unauthorized transactions. This real-world application highlights the practicality and significance of multisig.
The Future of Secure Digital Transactions
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of multisig in ensuring secure transactions becomes increasingly significant. Its adoption is not limited to cryptocurrencies; industries ranging from finance to supply chain management can benefit from the added security layers provided by multisig technology.


