Blockchain-Powered Identity Management for Enhanced Security
Identity management is undergoing a revolutionary transformation through the integration of blockchain technology. This article explores the significant advancements and enhanced security offered by implementing identity management on the blockchain.
The Evolution of Identity Management
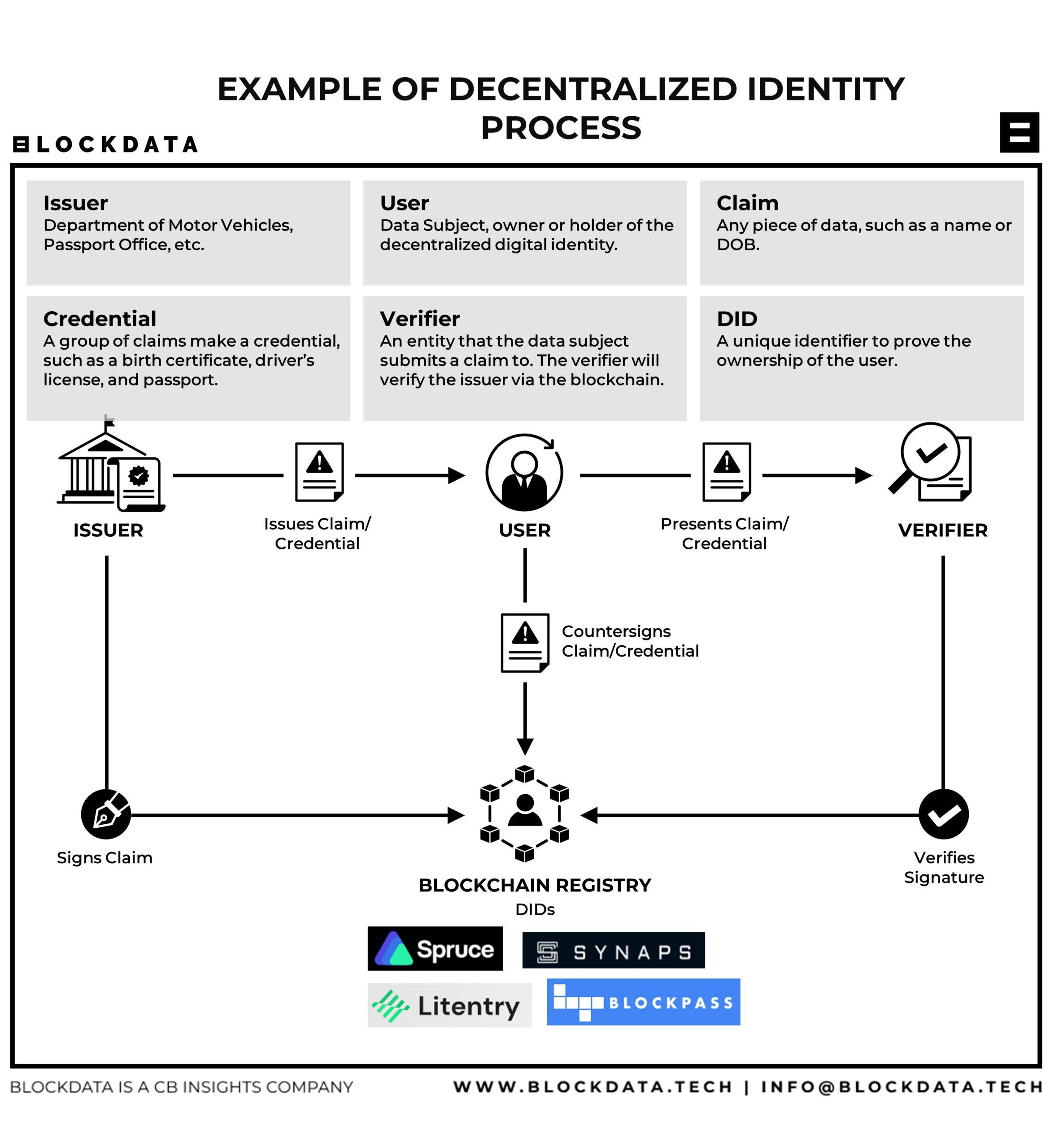
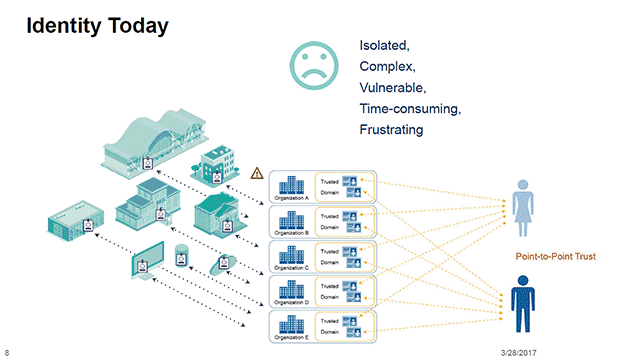
Traditional identity management systems often centralize user data, posing security and privacy risks. The rise of blockchain introduces a paradigm shift, empowering individuals to control their digital identity securely. Blockchain’s decentralized and tamper-resistant nature ensures a more robust foundation for identity management.
How Blockchain Secures Identity Data
Blockchain technology secures identity data through its decentralized architecture. Instead of relying on a single, vulnerable point of control, user information is distributed across a network of nodes. The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it becomes nearly impossible to alter, providing a high level of integrity and security.
Enhanced Privacy and User Control
Decentralized identity management on the blockchain prioritizes privacy and user control. Individuals have ownership of their identity data, deciding when and how it is shared. This shift from centralized control to user-centric control mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, fostering a more private and secure digital identity ecosystem.
Immutable Audit Trails for Identity Transactions
One key advantage of blockchain in identity management is the creation of immutable audit trails. Every transaction related to identity verification or authentication is recorded in a transparent and unalterable manner. This audit trail enhances transparency, making it easier to trace and verify the history of identity-related activities.
Smart Contracts Streamlining Identity Processes
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, streamline identity processes on the blockchain. They automate tasks such as identity verification, access control, and authorization, reducing the need for intermediaries and enhancing the efficiency of identity management workflows.
Interoperability Across Platforms and Services
Blockchain facilitates interoperability in identity management, allowing seamless interaction across various platforms and services. Users can employ their blockchain-based identity across different applications without redundant registrations. This not only simplifies user experiences but also reduces the risk associated with managing multiple sets of credentials.
Use Cases: From KYC to Healthcare
Blockchain-based identity management finds application in various sectors. Know Your Customer (KYC) processes in finance benefit from the enhanced security and efficiency offered by blockchain. Similarly, healthcare systems leverage blockchain for secure storage and sharing of electronic health records, ensuring patient data remains confidential and unaltered.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
Despite its advantages, implementing blockchain-based identity management poses challenges. Issues such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and standardization require careful consideration. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders are crucial to developing solutions that address these challenges and promote widespread adoption.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Blockchain Identity
The future of identity management on the blockchain holds exciting possibilities. Ongoing research and development are likely to bring forth innovations addressing current challenges and expanding the capabilities of blockchain identity solutions. Continued collaboration will play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of this transformative technology.
To learn more about the revolutionary