Pilot Green Hydrogen Technology: Innovating Sustainable Solutions
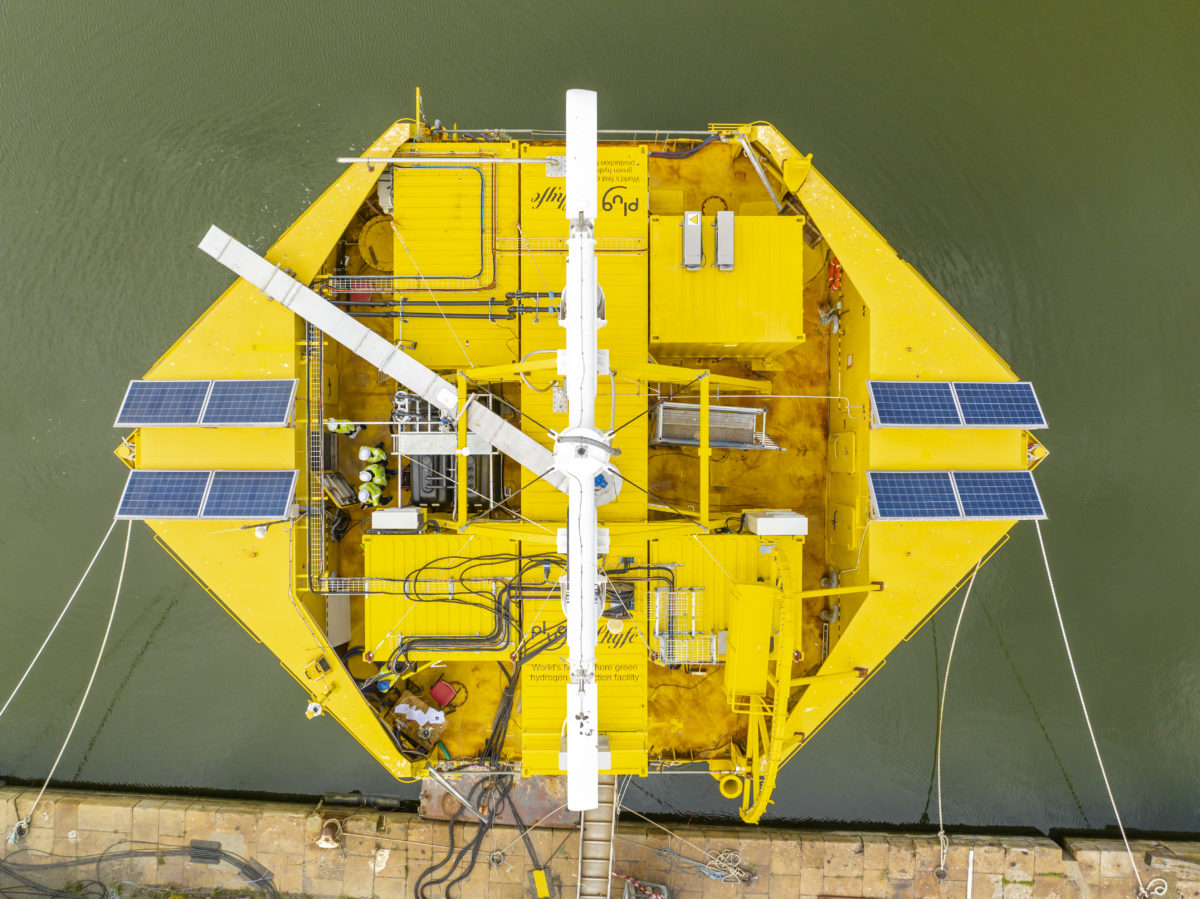
The emergence of pilot green hydrogen technology marks a significant milestone in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. This innovative approach to hydrogen production harnesses renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to produce hydrogen through electrolysis, offering a clean and versatile alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Advancing Renewable Energy Integration
Pilot green hydrogen technology represents a major step forward in the integration of renewable energy into the global energy system. By utilizing surplus renewable energy to power electrolyzers that split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, this technology helps to address the intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources. By storing excess renewable energy in the form of hydrogen, pilot green hydrogen technology enables a more reliable and resilient energy supply that can be deployed when needed, regardless of weather conditions or time of day.
Enabling Decarbonization Efforts
One of the primary benefits of pilot green hydrogen technology is its potential to support decarbonization efforts across various sectors. Hydrogen produced from renewable sources emits no greenhouse gases or pollutants when used as a fuel, making it a clean and sustainable energy carrier. In industries such as transportation, manufacturing, and heating, where decarbonization is particularly challenging, green hydrogen offers a viable pathway to reducing emissions and mitigating climate change impacts.
Fueling Transportation Innovation
The transportation sector is one of the key areas where pilot green hydrogen technology holds immense promise. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, which use hydrogen to generate electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen, offer a zero-emission alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. With advancements in fuel cell technology and infrastructure deployment, hydrogen-powered vehicles have the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry, providing long-range, fast refueling, and emission-free mobility solutions.
Powering Industrial Applications
In addition to transportation, pilot green hydrogen technology has applications across a wide range of industrial sectors. In industries such as steel and cement production, where high-temperature processes require large amounts of energy and emit significant carbon dioxide emissions, hydrogen can serve as a clean and efficient alternative fuel. By replacing fossil fuels with green hydrogen in industrial processes, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Overcoming Technical Challenges
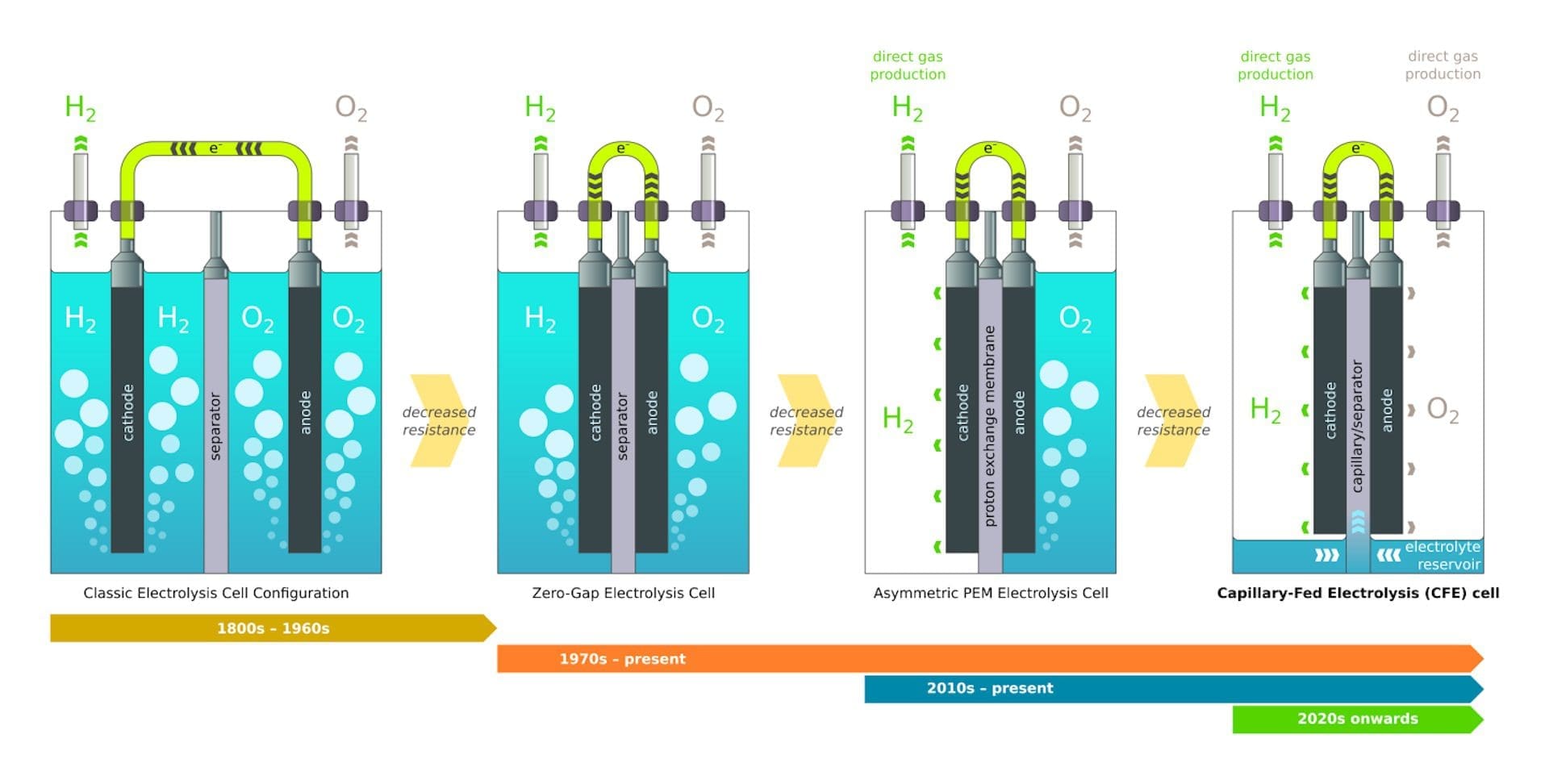
While pilot green hydrogen technology holds great promise, it also faces several technical challenges that must be addressed to achieve widespread adoption and scalability. One of the key challenges is reducing the cost of electrolysis, which remains a significant barrier to the commercialization of green hydrogen. Additionally, advancements are needed in hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructure to enable the widespread distribution and use of hydrogen as a fuel.
Scaling Up Deployment
Despite these challenges, efforts to scale up the deployment of pilot green hydrogen technology are underway around the world. Governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions are collaborating to invest in research, development, and demonstration projects aimed at accelerating the commercialization of green hydrogen technologies. By fostering innovation, driving down costs, and building the necessary infrastructure, stakeholders are