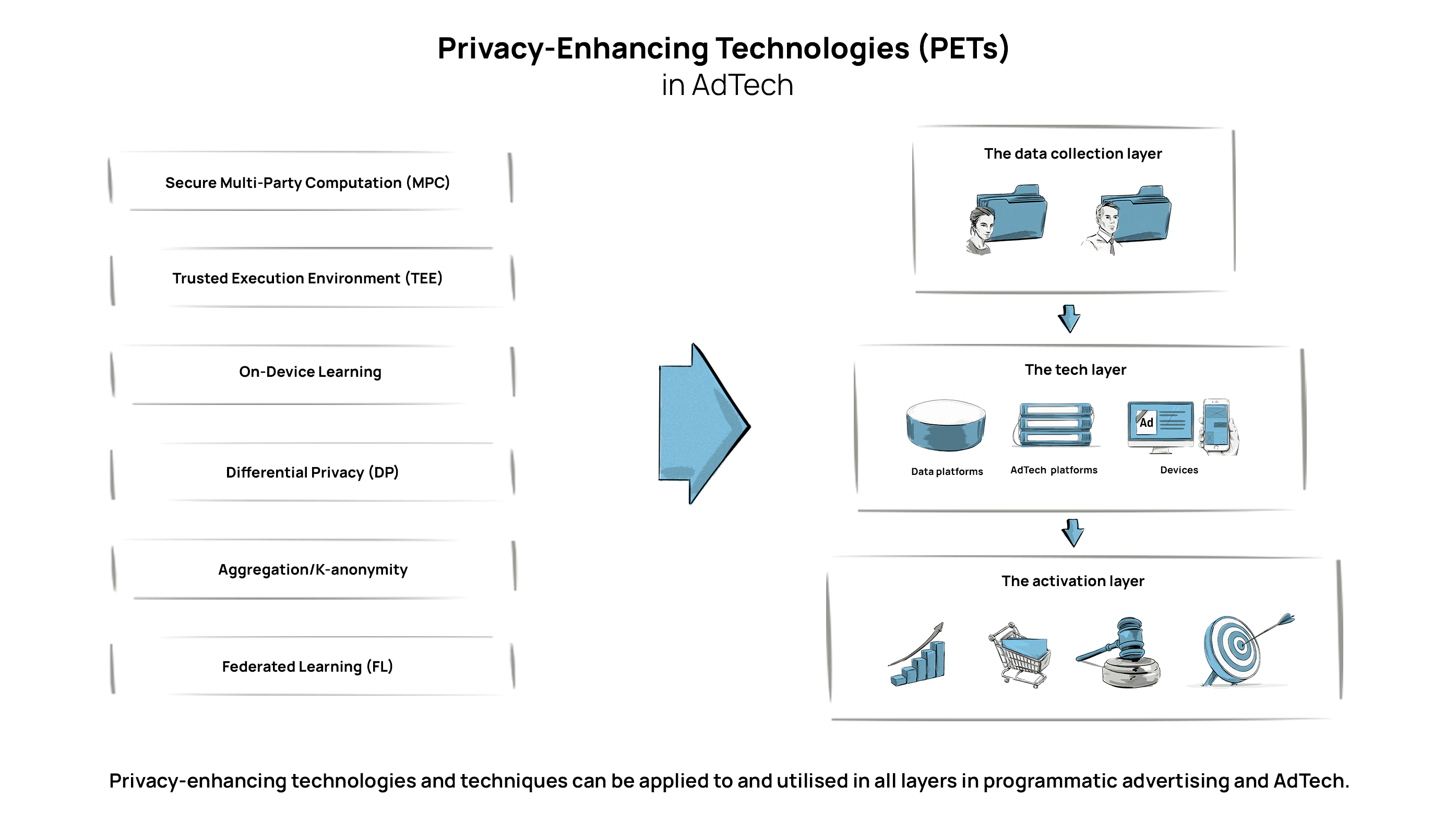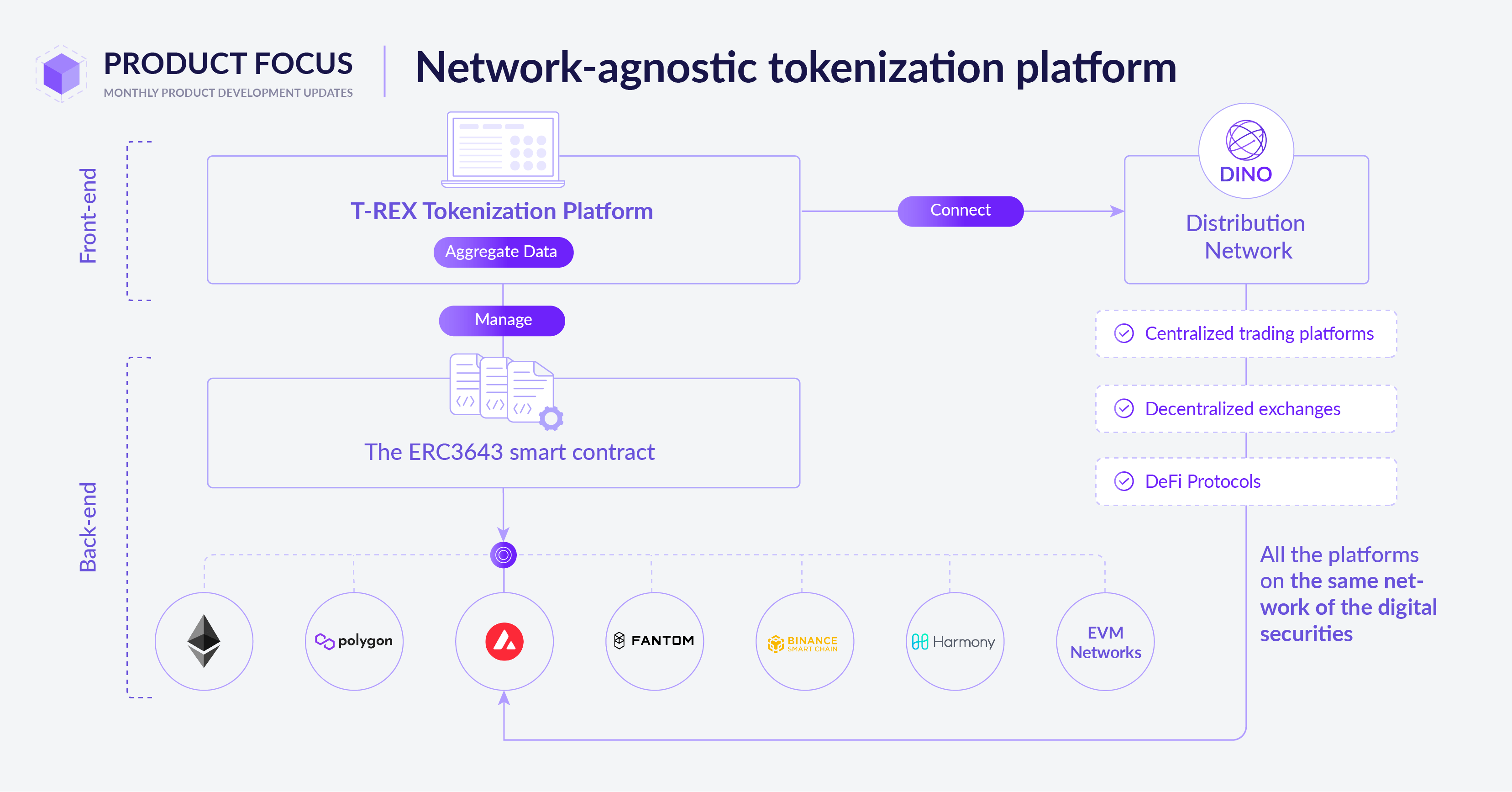
Understanding Security Tokenization
Security tokenization is a powerful strategy in the realm of cybersecurity, offering enhanced protection for sensitive data. This process involves converting sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or personal identifiers, into tokens. These tokens are unique, random values that retain no inherent meaning, providing a layer of security against potential breaches.
The Mechanics of Tokenization
In the tokenization process, sensitive data undergoes encryption and is replaced with a token that has no direct correlation to the original information. This ensures that even if a malicious actor gains access to the tokens, deciphering and exploiting them becomes an arduous task without the corresponding encryption keys. This sophisticated mechanism significantly reduces the risk of data exposure.
Benefits of Security Tokenization
1. Heightened Data Security
Security tokenization is a robust defense mechanism against data breaches. By eliminating the storage of actual sensitive information, even in secure databases, the potential damage from a breach is minimized. Tokens alone provide no valuable information to cybercriminals, rendering any compromised data useless without the proper decryption keys.
2. Compliance and Regulation
In an era of stringent data protection regulations, security tokenization aids organizations in meeting compliance requirements. By minimizing the storage of sensitive data, companies can navigate regulatory landscapes more effectively. Compliance with standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) becomes more achievable with the implementation of tokenization.
3. Streamlined Payment Processes
Security tokenization is widely used in the financial sector to secure online transactions. By tokenizing payment card information, businesses can facilitate secure transactions without exposing the actual card details. This not only safeguards customers but also streamlines payment processes, enhancing user experience.
Implementing Security Tokenization in Your System
1. Assessment of Sensitive Data
Before implementing security tokenization, organizations must conduct a thorough assessment of the types of sensitive data they handle. This includes personally identifiable information (PII), payment card data, and any other confidential details. Identifying and categorizing data sets help in determining the scope of tokenization.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating security tokenization into existing systems requires careful planning. Organizations should assess their current architecture and choose tokenization solutions that seamlessly integrate with their databases and applications. This integration ensures a smooth transition without disrupting daily operations.
3. Encryption Key Management
The security of tokenized data relies heavily on the management of encryption keys. Organizations must implement robust key management practices, including secure storage, regular rotation, and access controls. Proper key management enhances the overall security posture of the tokenization system.
Security Tokenization: A Link to Advanced Protection
To delve deeper into the world of security tokenization and its application in safeguarding sensitive information, explore Security tokenization. This comprehensive resource provides valuable insights, best practices, and the latest updates to empower organizations in fortifying their data security strategies.
In conclusion, security tokenization stands as a formidable defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By understanding its mechanics, appreciating the associated benefits, and implementing it effectively, organizations can elevate their security posture and instill