Securing Transactions: Exploring Sidechain Security Measures
Sidechains have emerged as a versatile solution to scalability issues in blockchain networks. This article delves into the importance of sidechain security and the measures implemented to ensure the integrity and safety of transactions within these off-chain solutions.
Understanding Sidechains and Their Role
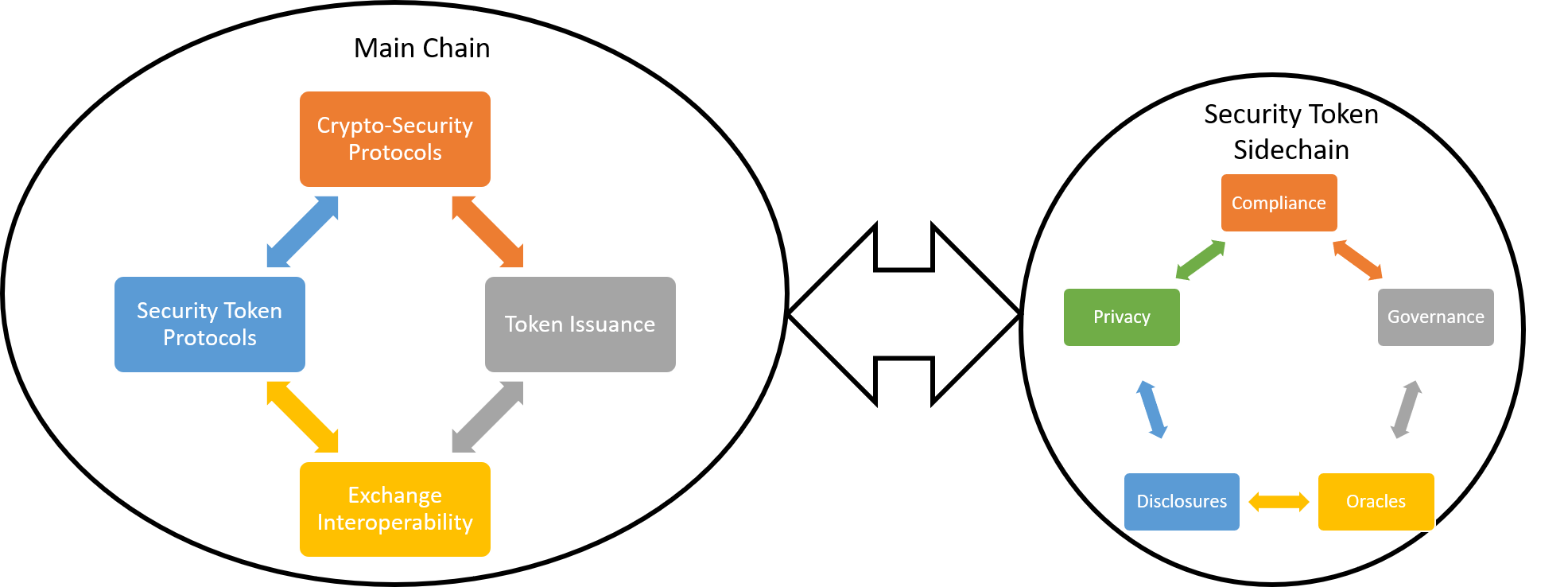
Sidechains are additional blockchains connected to a primary blockchain, allowing assets to be transferred between them. This architecture addresses scalability concerns by enabling certain transactions to occur off the main chain. While sidechains enhance scalability, their security is crucial to maintain the overall integrity of the blockchain network.
Importance of Sidechain Security
Sidechain security is paramount to the broader functionality and acceptance of blockchain networks. Since sidechains operate in conjunction with the main chain, any compromise in their security could have repercussions on the entire network. Therefore, implementing robust security measures within sidechains is essential to safeguard against potential vulnerabilities.
Cryptography and Encryption Protocols
One fundamental aspect of sidechain security is the utilization of strong cryptographic techniques and encryption protocols. These measures ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data transferred between the main chain and sidechains. By employing advanced cryptographic algorithms, sidechains can protect sensitive information and maintain secure transactions.
Consensus Mechanisms for Sidechains
Consensus mechanisms play a pivotal role in securing sidechains. While the main chain typically follows a specific consensus algorithm, sidechains may employ variations tailored to their specific needs. Implementing consensus mechanisms ensures that transactions on sidechains are valid, preventing malicious activities and maintaining the overall trust within the blockchain network.
Two-Way Pegging and Asset Security
Two-way pegging is a mechanism that enables assets to move seamlessly between the main chain and sidechains. Ensuring the security of this process is vital to prevent double-spending or unauthorized transfers. Security measures, such as cryptographic proofs and secure verification processes, are implemented to maintain the integrity of the pegging mechanism.
Decentralization and Network Nodes
Maintaining decentralization within sidechains is crucial for security. Distributing network nodes across various entities ensures that no single entity has undue control over the sidechain. Decentralization enhances security by reducing the risk of a single point of failure and mitigating the impact of potential attacks on the sidechain.
Smart Contracts and Security Audits
Smart contracts often play a significant role in sidechain functionality. Ensuring the security of these contracts is imperative to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Security audits, conducted by third-party experts, help identify and rectify any potential issues within smart contracts, contributing to the overall security of the sidechain.
Cross-Chain Communication Security
Interoperability between sidechains and the main chain requires secure cross-chain communication. Implementing secure communication protocols, such as hashed time-locked contracts (HTLCs), enhances the security of transactions moving between the main chain and sidechains. These measures prevent unauthorized access and ensure the proper execution of cross-chain transactions.
Regular Security Updates and Patching
The dynamic nature of the blockchain landscape necessitates continuous improvement in security measures. Regular updates and patching of software vulnerabilities are essential to address emerging threats. Sidechain operators must stay vigilant



