Empowering Collaboration: Essentials of Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains, a hybrid between public and private blockchains, offer a middle ground for organizations seeking collaborative and secure solutions. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of consortium blockchains, their advantages, use cases, and the collaborative power they bring to diverse industries.
Understanding Consortium Blockchains
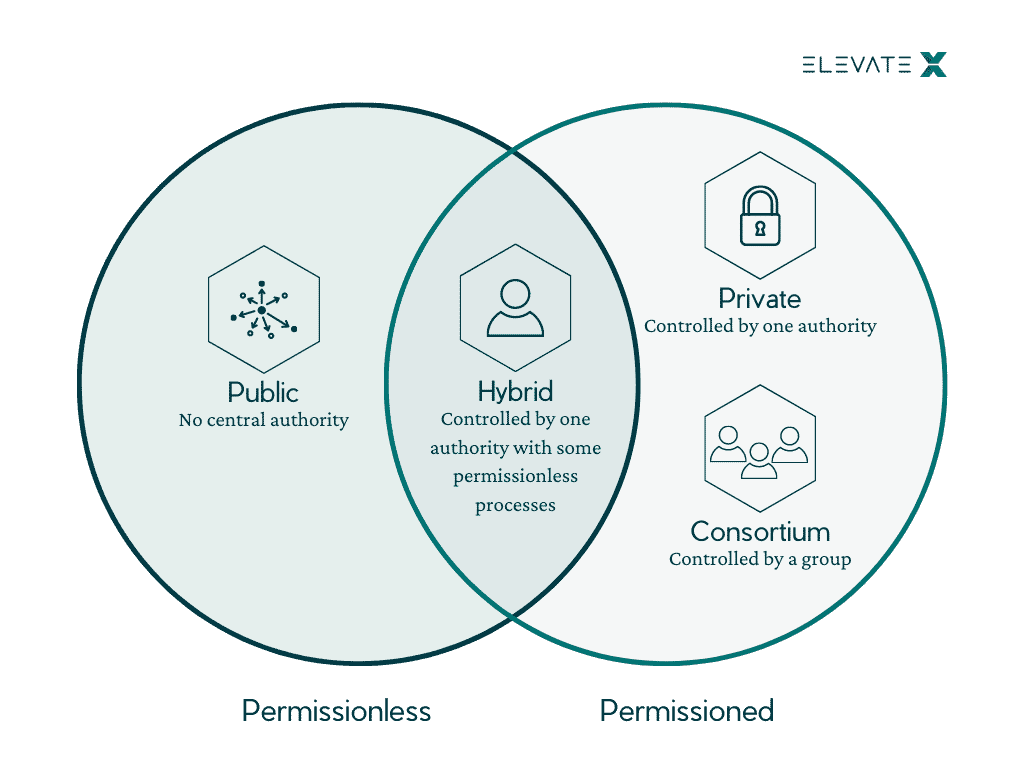
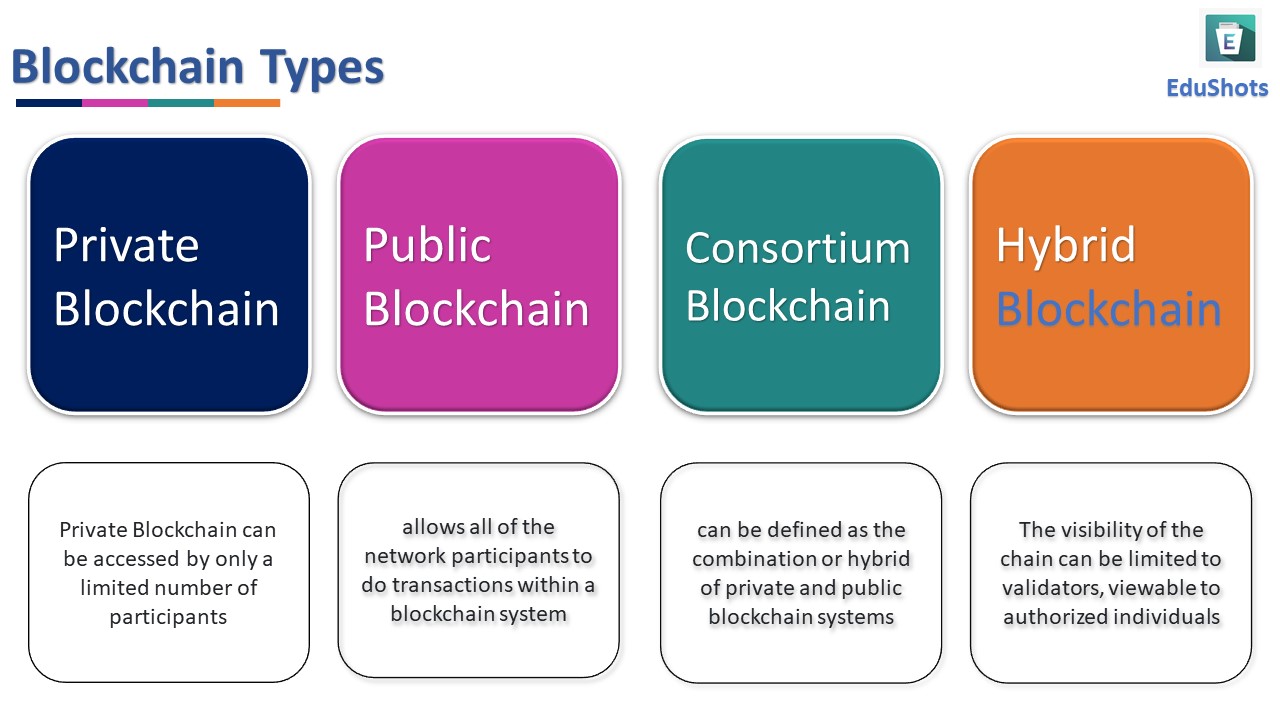
Consortium blockchains, also known as federated blockchains, involve a group of organizations forming a collaborative network with shared control over the blockchain. Unlike public blockchains, access is limited to a predefined set of participants, making it more private than public alternatives. This model strikes a balance between the openness of public blockchains and the exclusivity of private ones.
Advantages of Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains inherit advantages from both public and private models. Participants in the consortium have a shared interest in the success of the network, fostering trust among members. This shared control ensures that the blockchain remains decentralized and transparent while maintaining privacy and security, making it suitable for collaborative ventures.
Enhanced Security and Trust
Security is a paramount concern in any blockchain application, and consortium blockchains address this through collaborative security measures. The shared control among trusted participants minimizes the risk of malicious activities. This inherent trust among consortium members contributes to the overall security and reliability of the blockchain network.
Use Cases Across Industries
Consortium blockchains find applications across various industries due to their collaborative nature. In supply chain management, for instance, consortiums of manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors can use a blockchain to enhance traceability and transparency. In the financial sector, multiple banks may collaborate in a consortium blockchain for more efficient and secure interbank transactions.
Efficient and Streamlined Processes
Consortium blockchains streamline processes by providing a decentralized but controlled environment. With a predefined set of participants, consensus mechanisms can be more efficient, leading to quicker transaction confirmations. This efficiency is particularly crucial for industries requiring rapid and secure transactions among collaborating entities.
Interoperability and Standards
Interoperability is a significant advantage of consortium blockchains. Members within a consortium can agree upon standards for data and transactions, facilitating seamless collaboration. This interoperability ensures that diverse entities within the consortium can communicate and transact with each other efficiently, leading to more standardized and streamlined operations.
Cost Sharing and Resource Efficiency
Consortium blockchains offer cost-sharing benefits. Since multiple entities collaborate in maintaining the blockchain, the associated costs are distributed among participants. This resource-sharing model makes consortium blockchains a more cost-effective solution compared to individual entities developing and maintaining their private blockchains.
Challenges and Considerations
While consortium blockchains provide a collaborative solution, they come with challenges. Establishing governance structures, defining participation criteria, and addressing potential conflicts among members are critical considerations. Successful consortium blockchain implementation requires clear agreements and effective communication among all participating entities.
Future Trends and Evolution
The evolution of consortium blockchains is an ongoing process. As technology advances and industries adapt, consortium blockchains are likely to witness further refinement and widespread adoption. Future trends may include enhanced privacy features, increased scalability, and the development of