Navigating Digital Ledger Dynamics: Public and Private Blockchains
In the vast landscape of blockchain technology, two prominent variants, public and private blockchains, offer distinct advantages and serve diverse purposes. Let’s explore the dynamics of public and private blockchains, understanding their unique features and applications.
Understanding Public Blockchains
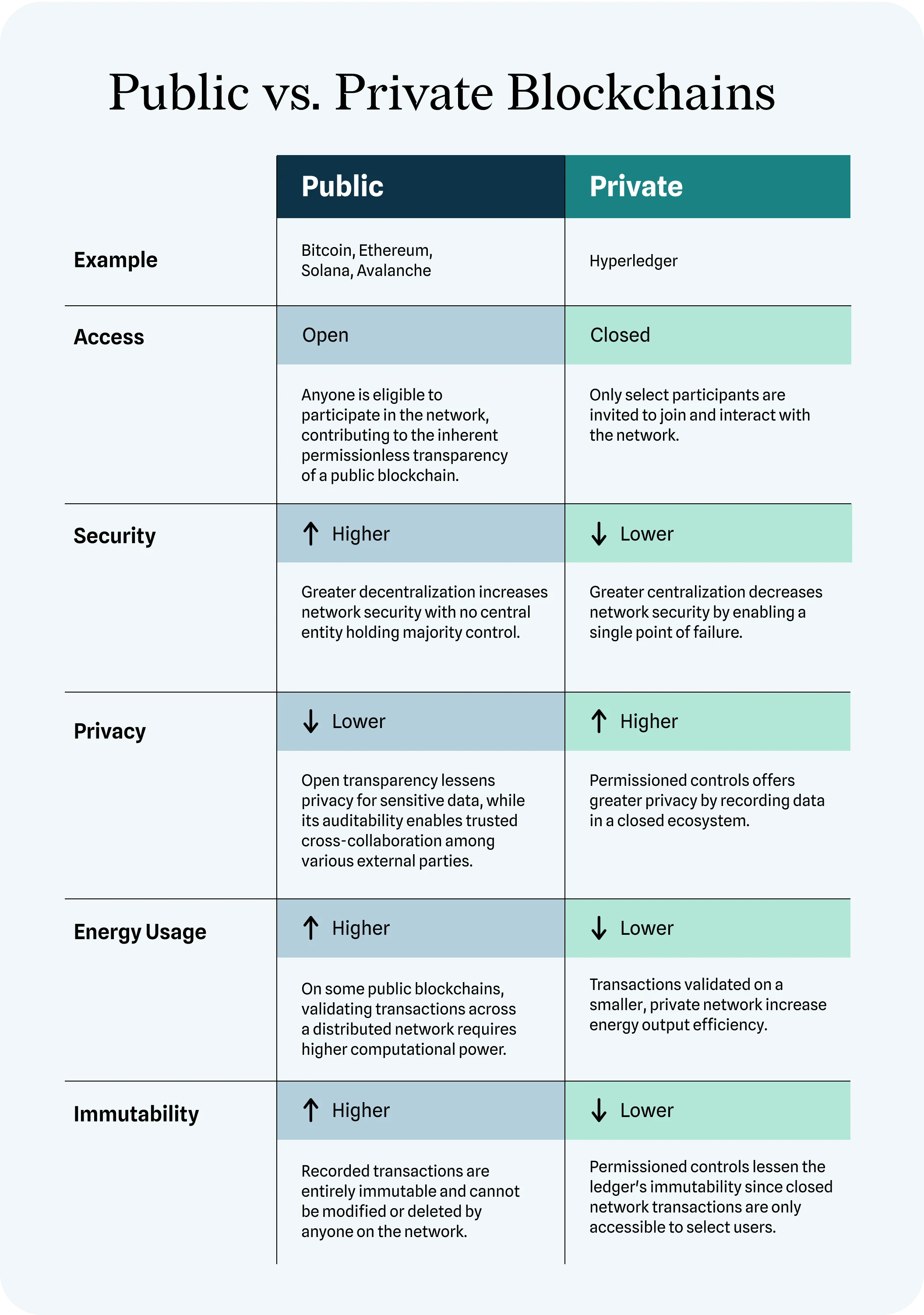
Public blockchains, exemplified by well-known platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum, operate on a decentralized network accessible to anyone. Participants can join, validate transactions, and contribute to the consensus mechanism. Transparency, security, and immutability are the hallmarks of public blockchains, making them ideal for scenarios requiring a trustless and open environment.
The Decentralized Nature of Public Blockchains
Public blockchains rely on a decentralized network of nodes, ensuring that no single entity has control. This decentralization fosters a high level of trust among participants, as transactions are collectively verified and recorded on the public ledger. The openness of public blockchains enhances security through transparency.
Applications of Public Blockchains
Public blockchains find extensive use in scenarios such as cryptocurrency transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized applications (DApps). These applications leverage the open and transparent nature of public blockchains, enabling secure and verifiable transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Challenges in Public Blockchains
Despite their advantages, public blockchains face challenges such as scalability and transaction speed. The consensus mechanisms, while ensuring security, can impact the efficiency of the network. These challenges drive ongoing research and development to enhance the performance of public blockchains.
Understanding Private Blockchains
In contrast, private blockchains restrict access to a specific group of participants. These participants are often known and vetted, providing a controlled environment. Privacy and permissioned access are key features of private blockchains, making them suitable for applications where a higher level of control is required.
Controlled Access in Private Blockchains
Private blockchains grant access only to authorized participants, allowing for a more controlled and efficient network. This control over participation makes private blockchains an attractive option for businesses and enterprises seeking to implement blockchain technology for internal processes.
Applications of Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are prevalent in industries such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare. These applications benefit from the increased control and privacy offered by private blockchains. Enterprises can implement blockchain technology for streamlined operations, secure record-keeping, and enhanced transparency within their closed ecosystems.
Challenges in Private Blockchains
While private blockchains address certain concerns of public counterparts, they face challenges related to trust. Participants in a private blockchain must have confidence in the governance structure and the entities involved. Achieving this trust requires careful planning and transparent communication among participants.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Public and Private Blockchains
In some cases, a hybrid approach combines elements of both public and private blockchains. This allows for the benefits of public blockchains’ transparency and security while maintaining control over access in certain areas. Hybrid models provide flexibility and cater to a wide range of use cases.
Choosing the Right Blockchain for Your Needs
Selecting between public and private blockchains depends on specific requirements. Public blockchains are suitable for open and trustless environments, while


