Compact Brilliance Samsung’s Small Phone Revolution The Rise of Small Phones: A Nostalgic Resurgence In a world dominated by oversized…
Read More

Compact Brilliance Samsung’s Small Phone Revolution The Rise of Small Phones: A Nostalgic Resurgence In a world dominated by oversized…
Read More
Introducing the Note 20 Ultra: Samsung’s Note 20 Ultra is not just a smartphone; it’s a symbol of luxury and…
Read More
Exploring the Next Frontier: A Deep Dive into Cloud Phone Android Unleashing Innovation: The Rise of Cloud Phone Android In…
Read More
Key Takeaways Understanding the basics of wrongful death claims can help you navigate the process more effectively. Gaining insights into…
Read More
Table of Contents Financial Security Tangible Asset Passive Income Appreciation Over Time Diversification of Investment Portfolio Positive Community Impact Financial…
Read More
Unlocking the Potential of SAS Programming Tips Mastering Data Analysis Techniques In the world of data science, SAS programming is…
Read More
Read more about riley hubatka…
Read More
Exploring Shiba Inu Blockchain: Unraveling the Potential Introduction: Shiba Inu and Blockchain In the world of cryptocurrency, Shiba Inu has…
Read More
Exploring the Digital Oasis of SK VIP Virtual Space Unlocking the Gateway to the Future In the ever-expanding landscape of…
Read More
Unveiling the Journey of Sienna Mae Gomez A Rising Star in the Making Sienna Mae Gomez, a name that’s been…
Read More
Green Innovation Examples: Pioneering Sustainability Revolutionizing Transportation Green innovation examples are reshaping the transportation sector, introducing sustainable alternatives to traditional…
Read More
Renewable Energy Storage Technology: Powering Sustainability Renewable energy storage technology stands at the forefront of sustainable energy solutions, offering a…
Read More
Exploring the Leading Hydrogen Electrolysis Companies Introduction to Hydrogen Electrolysis Hydrogen electrolysis has emerged as a key technology in the…
Read More
Lavo Green Energy Storage: Powering Sustainability Introducing the Lavo Green Energy Storage System, a cutting-edge solution revolutionizing the way we…
Read More
Sub Heading: Exploring the Cutting-Edge: Green Technology Examples Green technology examples exemplify the innovative solutions driving sustainability across various industries.…
Read More
Renewable Energy Battery Storage Companies: Powering Tomorrow Driving the Energy Transition In the midst of a global energy transition towards…
Read More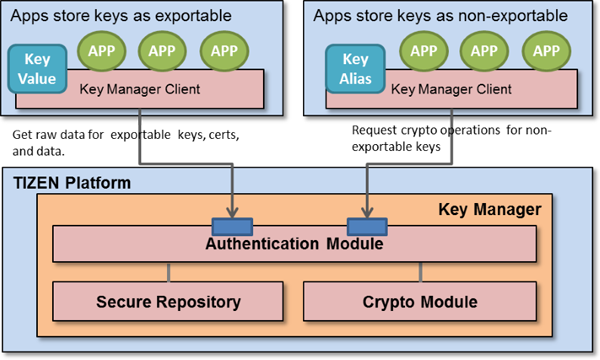
Ensuring Security: Best Practices in Key Management In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, secure key management stands as a…
Read More
Sub Heading: Pioneering Sustainability: Exploring Green Energy Technologies Green energy technologies are leading the charge towards a more sustainable and…
Read More
Revolutionizing Athletic Agreements: The Security of Tokenized Sports Contracts In the ever-evolving world of sports, the introduction of secure tokenized…
Read More
Ensuring Stability: The Security of Stablecoins Stablecoins, pegged to fiat currencies or commodities, have become essential in the cryptocurrency space,…
Read More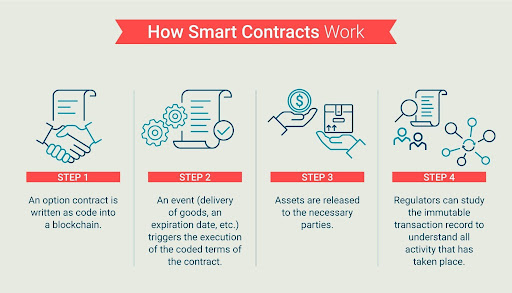
Smart Contract Audits: Ensuring Blockchain Code Security Blockchain technology relies heavily on smart contracts to automate and execute various functions…
Read More
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the concept of decentralization has gained significant prominence. From finance to governance, decentralized systems…
Read More
Navigating the Challenge: Understanding Double-Spending in Blockchain In the dynamic landscape of blockchain technology, the concept of double-spending poses a…
Read MoreThere is plenty that you should know about cell phones. Everything for best ways to buy to using them effectively.…
Read More