Navigating Digital Ledger Dynamics: Public and Private Blockchains In the vast landscape of blockchain technology, two prominent variants, public and…
Read More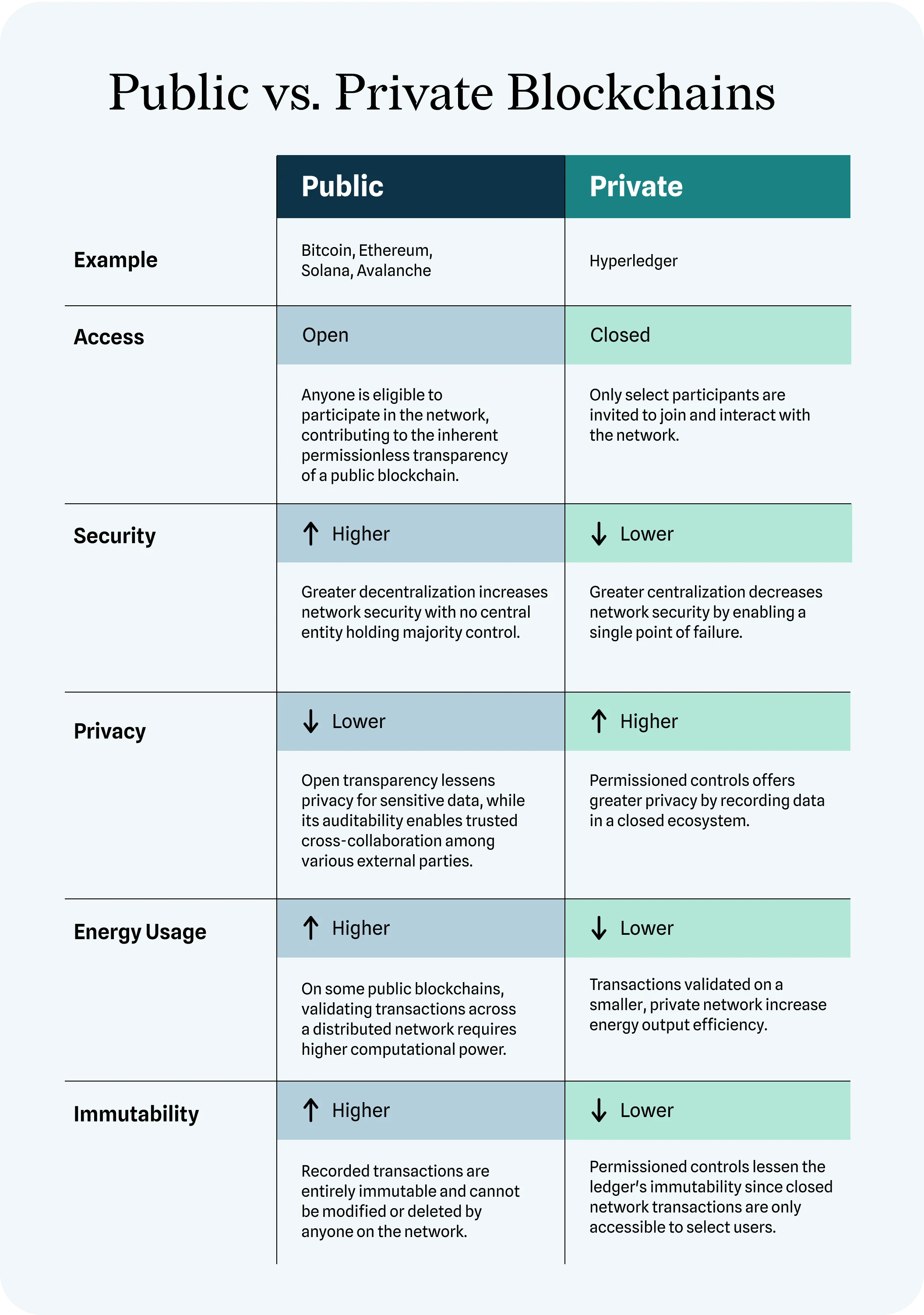

Navigating Digital Ledger Dynamics: Public and Private Blockchains In the vast landscape of blockchain technology, two prominent variants, public and…
Read More
Blockchain Confidentiality: Safeguarding Data in the Digital Ledger Blockchain technology, known for its transparency, also provides robust solutions for data…
Read More
Mastering Security: Essential Tips for Safeguarding Your Blockchain Blockchain technology, renowned for its security features, requires meticulous attention to ensure…
Read More