Unveiling Shibarium: Shiba Inu Coin’s Next Evolution A New Era Dawns In the ever-evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, Shiba Inu Coin…
Read More

Unveiling Shibarium: Shiba Inu Coin’s Next Evolution A New Era Dawns In the ever-evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, Shiba Inu Coin…
Read More
Unveiling Shibarium: The Future of Blockchain Technology A New Era Dawns In the fast-paced world of blockchain technology, innovation is…
Read More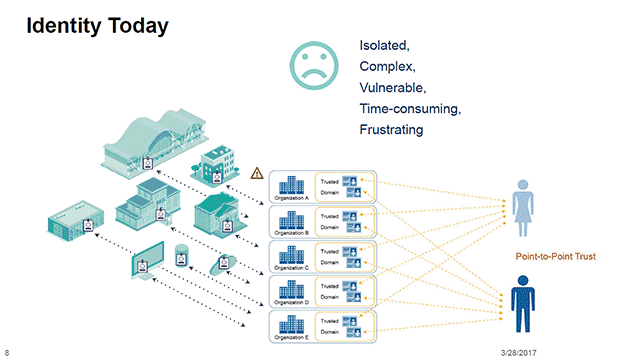
Blockchain-Powered Identity Management for Enhanced Security Identity management is undergoing a revolutionary transformation through the integration of blockchain technology. This…
Read More
Navigating the Landscape: Blockchain Interoperability Standards The blockchain ecosystem, with its decentralized and distributed nature, has revolutionized various industries. However,…
Read More
Empowering the Future of Decentralized Finance: Exploring Cardano (ADA) In the landscape of blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi), Cardano (ADA)…
Read More
Advancing Enterprise Solutions: The Power of Hyperledger Blockchain Blockchain technology has evolved beyond its origins in cryptocurrencies, finding profound applications…
Read More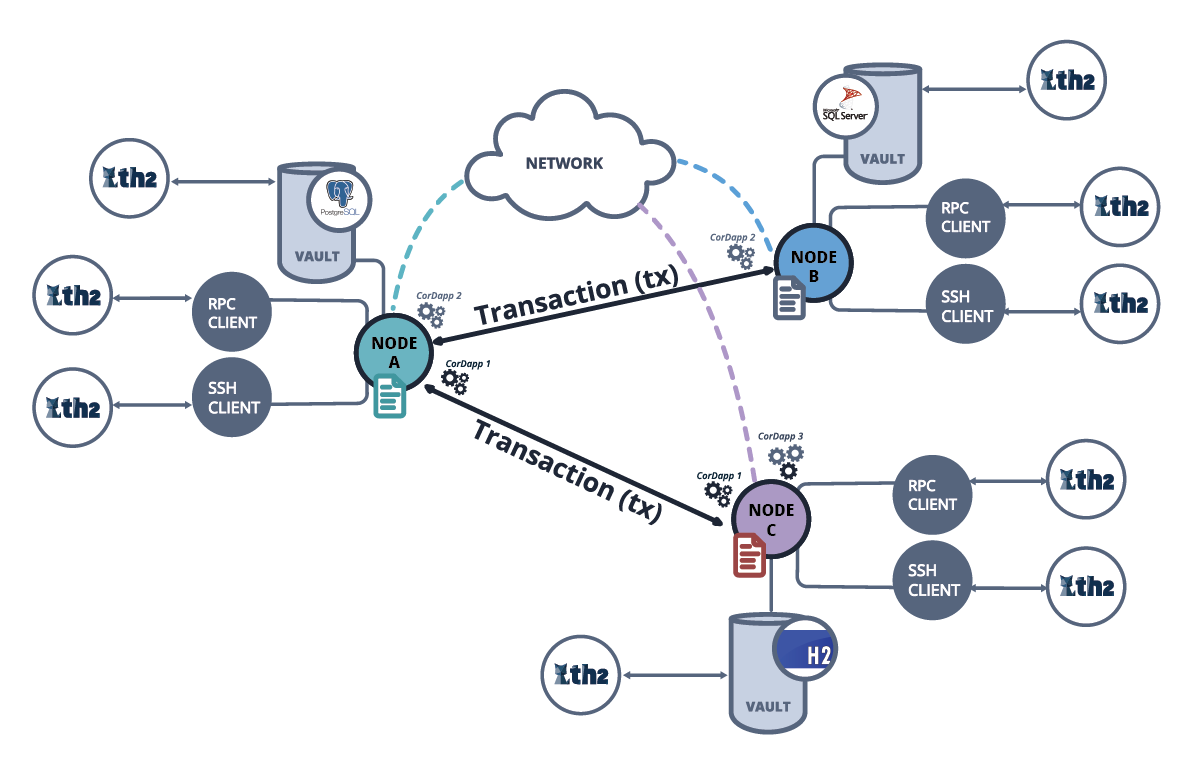
Transforming Records: A Dive into Distributed Ledger Technology Exploring the realm of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) reveals a paradigm shift…
Read More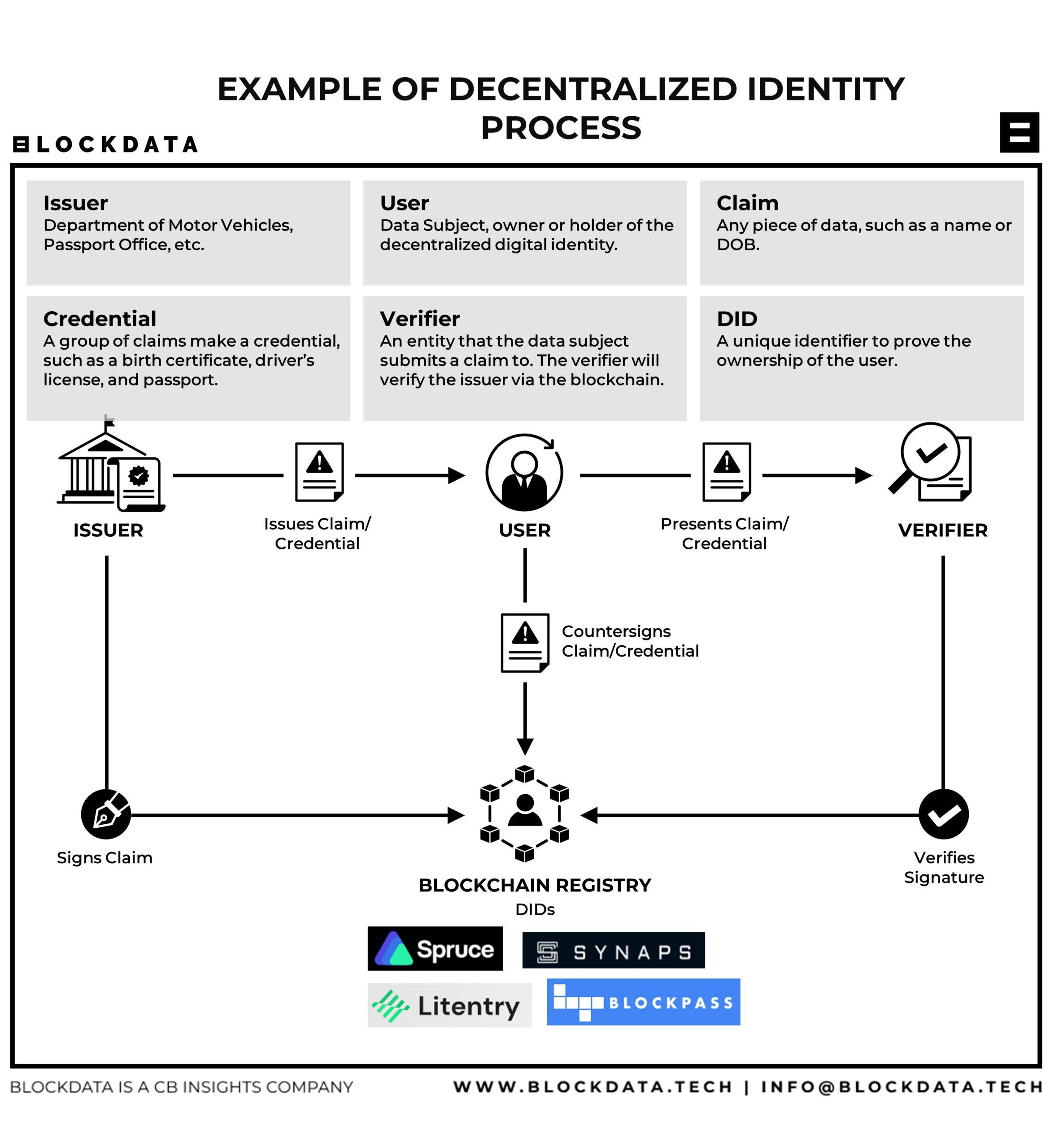
Empowering Users in the Digital Realm with Decentralized Identity Decentralized identity is revolutionizing the way individuals interact and assert their…
Read More