Introducing Starlight iPhone 13: In the ever-evolving world of smartphones, Apple has once again raised the bar with the introduction…
Read More

Introducing Starlight iPhone 13: In the ever-evolving world of smartphones, Apple has once again raised the bar with the introduction…
Read More
Introducing the Samsung Galaxy A20s: Samsung has long been synonymous with innovation and excellence in the world of smartphones. With…
Read More
Introducing the Nothing Phone: In a world where smartphones are becoming increasingly expensive, Nothing, a London-based tech startup, has set…
Read More
Introduction: Redefining Fitness Tracking In today’s fast-paced world, staying fit and healthy has never been more important. With the T-Mobile…
Read More
Introducing the iPhone 13 Pro Black Edition: The iPhone 13 Pro Black Edition is not just a smartphone; it’s a…
Read More
Introduction Are you on the hunt for the perfect iPhone watch that complements your style? Look no further! In this…
Read More
Introduction: A New Era of Innovation In the ever-evolving world of technology, Apple has once again raised the bar with…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing the Apple iPhone 8 Plus In the ever-evolving world of smartphones, Apple continues to set the standard with…
Read More
Introduction: In a world where smartphones have become an integral part of our daily lives, finding the right device to…
Read More
Unveiling the Journey of Sienna Mae A Glimpse into Sienna Mae’s World Sienna Mae, a rising star in the world…
Read More
Subheading: Introduction to the Latest Google Phone The tech world is abuzz with excitement as Google unveils its latest masterpiece…
Read More
Unveiling the Galaxy S20 Ultra 5G: A Game-Changer in Mobile Technology In a world where innovation knows no bounds, Samsung…
Read More
Exploring Pull & Bear’s Virtual Fashion Landscape Immerse Yourself in the Pull & Bear Metaverse Experience In the ever-evolving landscape…
Read More
Unlocking the Potential of RBC Crypto In the dynamic realm of digital finance, RBC Crypto emerges as a promising contender,…
Read More
Exploring Shardeum Blockchain: The Future of Digital Transactions Revolutionizing Digital Transactions Shardeum Blockchain emerges as a beacon of innovation in…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing the Samsung Galaxy A52 In a world where smartphones are indispensable tools for both work and play, the…
Read More
Unveiling the Secrets of Refactoring Tips Understanding the Importance of Refactoring In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, maintaining clean…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing the Fast Charging Solution for Samsung S22 In a world where our smartphones are our lifelines, having a…
Read More
Introducing the Samsung Galaxy S21: Elevating Experiences The Next Generation Unveiled In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Samsung has consistently…
Read More
Embarking on the Journey Quenlin Blackwell, a name that resonates across the digital landscape, signifies not just a person but…
Read More
Shiloh Jolie Pitt’s TikTok Journey Unveiled Introduction: Shiloh Jolie Pitt, the daughter of Hollywood stars Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt,…
Read More
Shermin Voshmgir: A Trailblazer in Blockchain Innovation Introducing Shermin Voshmgir: The Blockchain Visionary In the ever-evolving realm of blockchain technology,…
Read More
The Radiant Glow of Blockchain Innovation In the realm of digital finance, Radiant Blockchain shines brightly as a beacon of…
Read More
Discovering Samsung’s Online Store: A Tech Wonderland In today’s fast-paced world, technology is an integral part of our daily lives.…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing Samsung SmartThings In a world where technology continues to evolve, Samsung SmartThings emerges as a beacon of innovation,…
Read More
Introducing the Samsung Galaxy A10e Affordable Excellence In a world where smartphones seem to be getting more expensive by the…
Read More
The Early Days: A Glimpse into Quinton Griggs’ Beginnings Quinton Griggs, a name now synonymous with digital influence, had humble…
Read More
Speed Up Python Loops with List Comprehensions Mastering Array Manipulation in JavaScript When it comes to manipulating arrays in JavaScript,…
Read More
Unleash Your Python Skills with Clever Code Tricks Mastering Python Efficiency In the world of programming, mastering Python efficiency is…
Read More
Introduction Cryptocurrency has evolved significantly since the inception of Bitcoin over a decade ago. While Bitcoin laid the foundation, numerous…
Read More
Exploring Quorum Crypto: Revolutionizing Digital Transactions The Evolution of Quorum Crypto In the fast-paced world of digital finance, Quorum Crypto…
Read More
Exploring the Artistry of Soggyalien22 Introduction: A Glimpse into the Creative Cosmos Enter the realm of Soggyalien22, where imagination knows…
Read More
Exploring Sensorium Metaverse: A Virtual Reality Revolution Immersive Entertainment Experience Sensorium Metaverse is revolutionizing the virtual reality (VR) landscape by…
Read More
Unveiling Expert Tips for Beginner Software Developers Introduction: Embarking on Your Software Development Journey So, you’ve decided to dive into…
Read More
Unlocking Pythonic Programming Mastery Understanding Pythonic Programming Pythonic programming is more than just writing code in Python—it’s about adopting a…
Read More
Exploring the Intersection of Siri and Virtual Reality Introduction Virtual Reality (VR) has rapidly emerged as a transformative technology, offering…
Read More
Unveiling the Wisdom of the Python Tips Book Introduction: Navigating the Python Landscape In the vast world of programming, Python…
Read More
Exploring Selfridges Metaverse: The Future of Retail Immersive Shopping Experiences Selfridges Metaverse represents a groundbreaking shift in the world of…
Read More
Exploring the Potential of the Real Metaverse The Future of Virtual Worlds In recent years, the concept of the metaverse…
Read More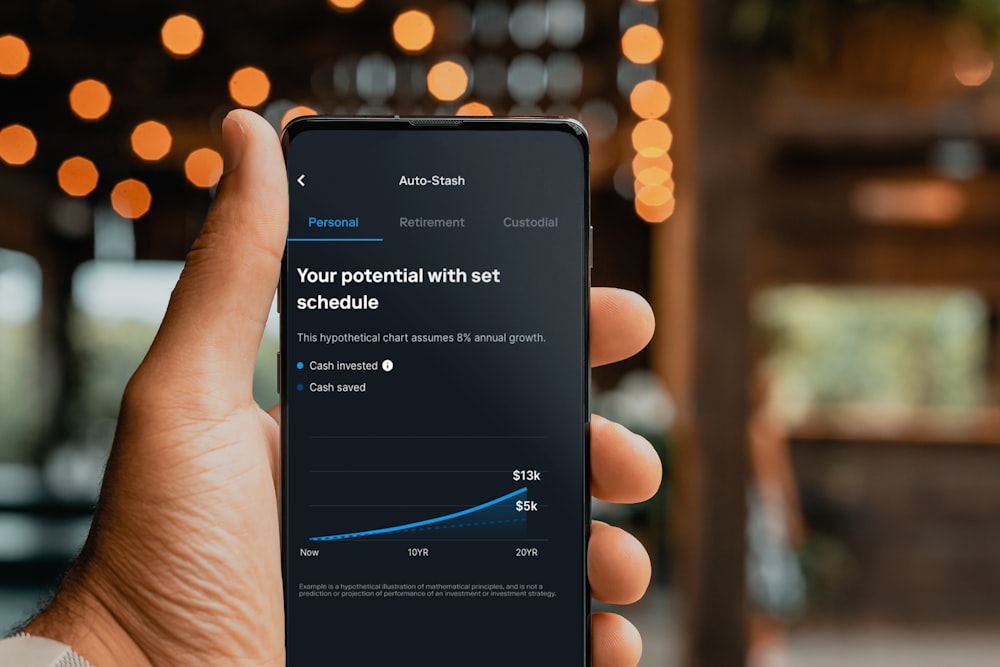
Exploring the Future of Finance with RBC Crypto Understanding RBC Crypto In the dynamic landscape of digital finance, RBC Crypto…
Read More
Exploring the Legacy of Romeo Catacutan Introduction: A Leader Ahead of His Time Romeo Catacutan, a name synonymous with innovation…
Read More
Offshore Hydrogen Production: The Future of Clean Energy Offshore hydrogen production represents a groundbreaking frontier in the quest for sustainable…
Read More
Eco-Friendly Innovations: Sustainable Building Materials In the realm of construction and architecture, the quest for sustainable solutions has become paramount.…
Read More
Sustainable Energy Technology: Powering Tomorrow In the quest for a cleaner and more sustainable future, sustainable energy technology emerges as…
Read More
Empowering a Greener Future with Sustainable Energy Solutions Meeting Global Energy Demands As the world’s population continues to grow and…
Read More
Revolutionizing Clean Energy: The Industrial Hydrogen Electrolyzer In the realm of clean energy, the industrial hydrogen electrolyzer emerges as a…
Read More
Driving Sustainability Forward: Innovative Renewable Energy Products Championing Innovation in Renewable Energy Innovative renewable energy products are at the forefront…
Read More
Exploring innovative green building technology examples unveils a range of sustainable solutions revolutionizing the construction industry. Let’s delve into some…
Read More
Unveiling the Power of Green Hydrogen Electrolysis Understanding Green Hydrogen Green hydrogen, often hailed as the fuel of the future,…
Read More
Exploring the Cost of Hydrogen Electrolyzers Understanding Hydrogen Electrolyzers Hydrogen electrolyzers are essential components of green energy systems, converting electricity…
Read More