Unveiling the Innovation: Samsung Galaxy Edge Explained The Design: A Visual Marvel The Samsung Galaxy Edge is not just another…
Read More

Unveiling the Innovation: Samsung Galaxy Edge Explained The Design: A Visual Marvel The Samsung Galaxy Edge is not just another…
Read More
Unlocking the Potential of Riot Crypto Introduction: Exploring the World of Cryptocurrency In recent years, cryptocurrency has emerged as a…
Read More
Rediscovering the Classic: A Look at the Blackberry Passport Revolutionizing the Smartphone Landscape The Blackberry Passport has emerged as a…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing the Apple Watch SE Nike Edition In the fast-paced world of fitness technology, Apple and Nike have once…
Read More
Mastering Python Efficiency Unleashing the Power of Python In the realm of programming, Python stands out as one of the…
Read More
Unlocking the Power of SmartIR Home Assistant Introducing SmartIR Home Assistant: A Game-Changer in Home Automation In today’s fast-paced world,…
Read More
Innovations in renewable energy sources are shaping the future of sustainable power generation, offering promising solutions to the challenges of…
Read More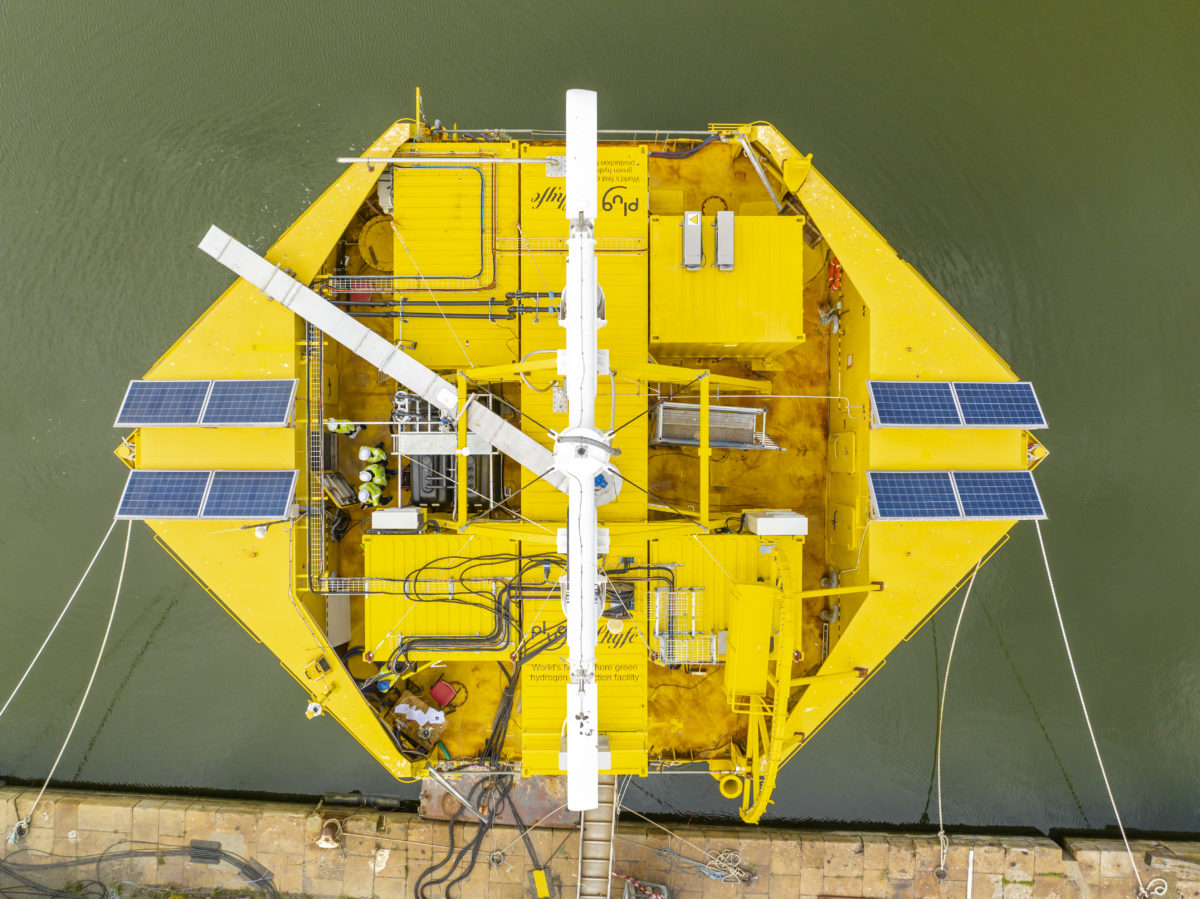
Pilot Green Hydrogen Technology: Innovating Sustainable Solutions The emergence of pilot green hydrogen technology marks a significant milestone in the…
Read More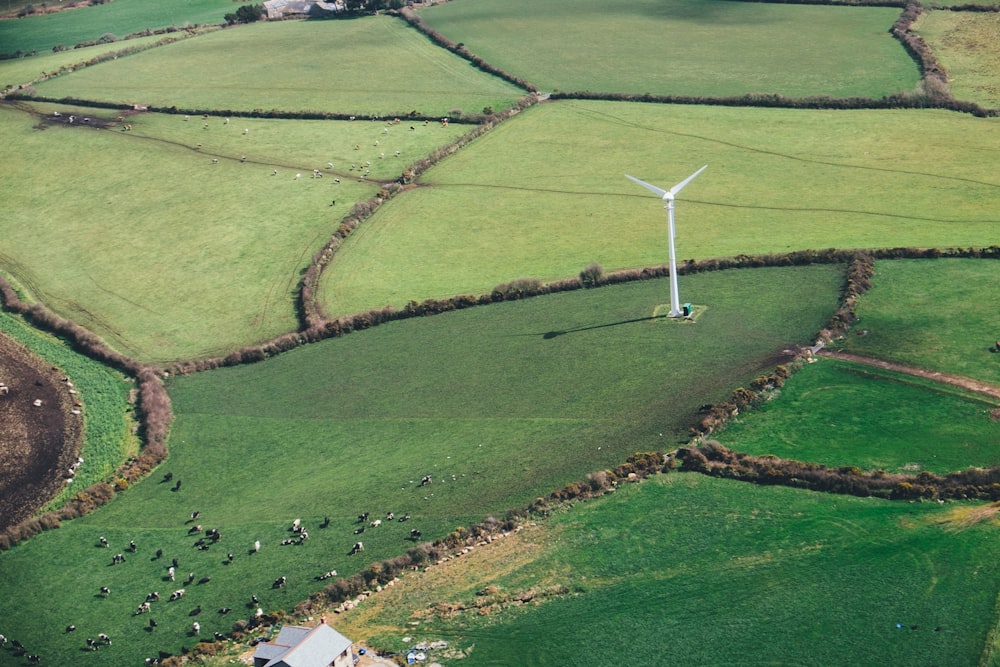
Green Hydrogen Power: Fueling a Sustainable Future Harnessing Clean Energy Green hydrogen power is emerging as a transformative force in…
Read More
Fostering Sustainable Innovation: Green Tech Gatherings The Significance of Green Tech Events Green tech events play a vital role in…
Read More
Driving Innovation: The Role of Renewable Energy Tech Companies Renewable energy tech companies are at the forefront of revolutionizing the…
Read More
Privacy-Preserving Innovation in Cryptocurrency: Unveiling Zcash (ZEC) Embarking on the landscape of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, Zcash (ZEC) stands as a pioneer…
Read More
SocialGuard: Reinventing Secure Decentralized Social Connections In an era dominated by digital interactions, the security and privacy of social connections…
Read MoreRenewable energy resources encompass a diverse array of sustainable options, each offering unique benefits and applications. Let’s delve into the…
Read More
Unlocking Security: Navigating Through Bug Bounty Programs Bug bounty programs have become integral in the cybersecurity landscape, providing a proactive…
Read More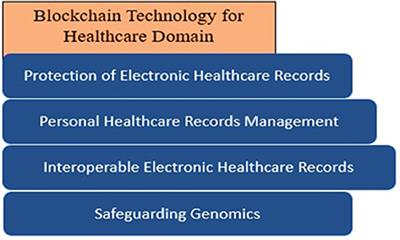
Securing Healthcare Records: Blockchain’s Trusted Data Integrity Healthcare records hold sensitive and vital information, making the security of these records…
Read More
Understanding the Imperative of Malware Resistance Malware resistance is a critical facet of cybersecurity, representing the collective efforts to fortify…
Read More
Revolutionizing Digital Currency Transactions: Exploring Bitcoin In the dynamic landscape of digital currencies, Bitcoin stands as a trailblazer, redefining how…
Read More
Global Security: Tokenized Cross-Border Transactions for Trust In an interconnected global economy, cross-border transactions are the lifeblood of international trade.…
Read More
Navigating the Secure Landscape of Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) Decentralized exchanges (DEX) have become pivotal in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering users…
Read More
Revolutionizing Energy Transactions: The Security of Tokenized Contracts In the rapidly evolving landscape of the energy sector, the introduction of…
Read More
Mastering Security: Essential Tips for Safeguarding Your Blockchain Blockchain technology, renowned for its security features, requires meticulous attention to ensure…
Read More