Exploring the Power of Green Technology
Harnessing Renewable Resources
Green technology utilizes renewable resources to create eco-friendly products and solutions that benefit both people and the planet. By tapping into the abundant and sustainable energy sources provided by nature, such as sunlight, wind, water, and biomass, green technology offers innovative ways to meet our needs while minimizing environmental impact. From renewable energy systems to sustainable materials and efficient processes, green technology is transforming industries and driving progress towards a more sustainable future.
Renewable Energy Systems
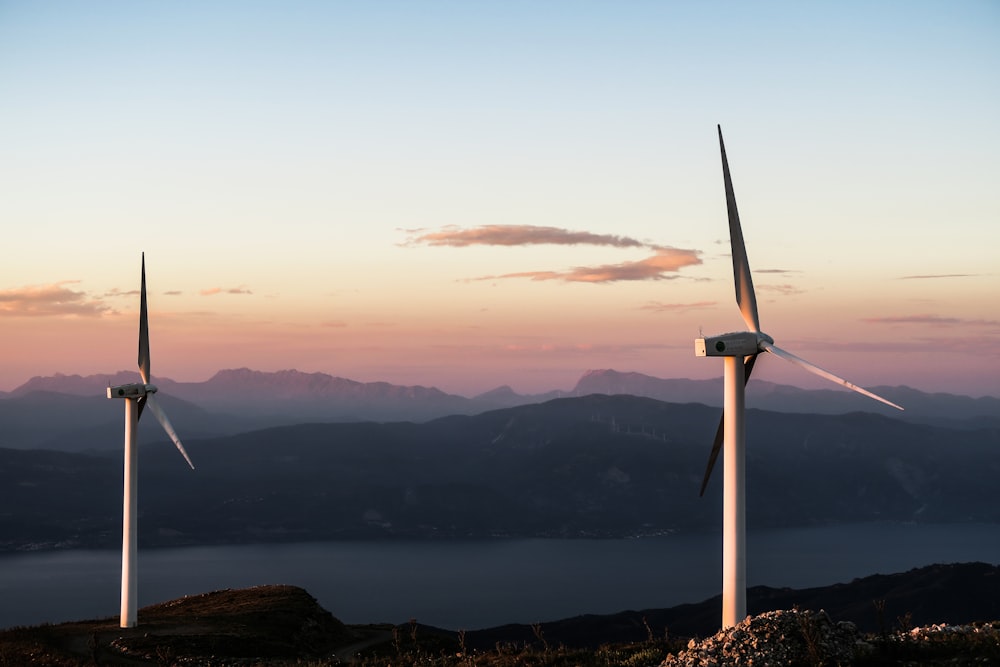
At the heart of green technology lies the use of renewable energy systems, which harness the power of nature to generate clean electricity. Solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, hydroelectric dams, and geothermal power plants are just a few examples of renewable energy technologies that produce electricity without emitting harmful greenhouse gases or depleting finite resources. These systems provide a reliable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Sustainable Materials and Products
In addition to renewable energy, green technology encompasses the development of sustainable materials and products that minimize resource consumption and waste generation. From biodegradable plastics and eco-friendly packaging to sustainable building materials and organic textiles, there is a growing demand for products that are both environmentally friendly and socially responsible. By prioritizing sustainability throughout the product lifecycle, green technology is driving innovation and promoting a circular economy that conserves resources and reduces pollution.
Efficient Resource Management
Green technology also focuses on optimizing resource management through efficient processes and technologies that minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. Energy-efficient appliances, smart building systems, and water-saving technologies are just a few examples of innovations that help reduce resource consumption and lower environmental impact. By adopting these technologies, businesses and individuals can lower their operating costs, improve efficiency, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Clean Transportation Solutions
Transportation is another area where green technology is making significant strides towards sustainability. Electric vehicles powered by renewable energy offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles, reducing air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, advancements in public transportation systems, shared mobility services, and alternative fuels are further reducing emissions and congestion in urban areas, making transportation more sustainable and accessible for all.
Environmental Monitoring and Conservation
Green technology also plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring and conservation efforts, helping to protect ecosystems and biodiversity. Remote sensing technologies, geographic information systems (GIS), and data analytics tools enable scientists and conservationists to monitor and manage natural resources more effectively, identifying environmental threats and implementing conservation measures. By leveraging these technologies, we can better understand and protect our planet’s natural resources for future generations.
Empowering Communities
One of the key principles of green technology is community empowerment, ensuring that the benefits of sustainability are accessible to all. By providing access to clean energy, clean water, and sustainable livelihoods, green technology helps improve the quality of life for communities around the world, particularly those most vulnerable to