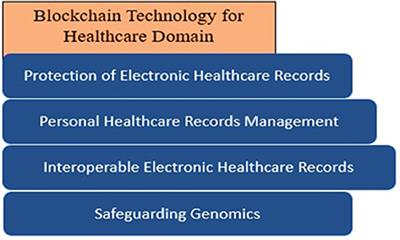
Securing Healthcare Records: Blockchain’s Trusted Data Integrity
Healthcare records hold sensitive and vital information, making the security of these records paramount. The integration of blockchain technology introduces a revolutionary approach to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of healthcare data. This article explores the transformative impact of securing healthcare records on the blockchain.
The Significance of Data Security in Healthcare
Data security is a critical concern in the healthcare industry, given the sensitivity of patient information. Breaches can lead to severe consequences, compromising patient privacy and trust. Blockchain, with its inherent security features, offers a robust solution to fortify healthcare data against unauthorized access, tampering, and breaches.
Blockchain’s Immutable Ledger for Patient Records
Blockchain’s primary strength lies in its immutability. Each healthcare transaction, from patient consultations to diagnostic tests and treatment plans, is securely recorded on an immutable ledger. This ensures that once information is added, it cannot be altered, providing an accurate and unchangeable history of patient records.
Enhancing Patient Privacy through Cryptography
Cryptography plays a pivotal role in securing healthcare records on the blockchain. Patient identities and medical histories are encrypted, ensuring that only authorized individuals, such as healthcare providers and the patients themselves, can access the information. This cryptographic layer adds an extra level of protection against unauthorized disclosure.
Interoperability for Comprehensive Healthcare Records
Blockchain promotes interoperability by enabling seamless data sharing across different healthcare providers. This interconnectedness allows for a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, regardless of where the data originated. The result is improved care coordination, reduced redundancies, and better-informed medical decisions.
Smart Contracts Automating Healthcare Processes
Smart contracts automate various healthcare processes, streamlining administrative tasks and reducing the risk of errors. Appointment scheduling, insurance claims processing, and billing can be executed automatically based on predefined rules. This not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the potential for fraud or billing discrepancies.
Securing Telemedicine Transactions
In the era of telemedicine, where remote consultations and virtual care are prevalent, ensuring the security of healthcare transactions is crucial. Blockchain provides a secure and transparent platform for recording telemedicine interactions, preserving the integrity of patient-doctor communications and treatment plans.
Auditable Trails for Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a significant aspect of healthcare operations. Blockchain’s auditable trails facilitate compliance by providing transparent records of all transactions. This transparency simplifies the auditing process, ensuring that healthcare providers adhere to regulatory requirements and standards.
Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain Adoption
While the benefits are compelling, the adoption of blockchain in healthcare faces challenges. Issues like scalability, standardization, and the integration with existing systems need careful consideration. Collaborative efforts among healthcare stakeholders and ongoing technological advancements are essential for overcoming these challenges.
Pilots and Success Stories in Healthcare Blockchain
Numerous pilot projects and successful implementations of blockchain in healthcare showcase the feasibility and effectiveness of this technology. From securing patient data to improving pharmaceutical supply chain transparency, these initiatives demonstrate the transformative potential of blockchain in the healthcare sector.
The Future Landscape of Healthcare Data Security
As technology continues to