The Radiant Glow of Blockchain Innovation In the realm of digital finance, Radiant Blockchain shines brightly as a beacon of…
Read More

The Radiant Glow of Blockchain Innovation In the realm of digital finance, Radiant Blockchain shines brightly as a beacon of…
Read More
Discovering Samsung’s Online Store: A Tech Wonderland In today’s fast-paced world, technology is an integral part of our daily lives.…
Read More
Where Performance Meets Portability: Unveiling the Samsung Tab S7 Lite Unveiling the Marvel: Introducing the Samsung Tab S7 Lite In…
Read More
Unleash Your Imagination In a world where technology continually evolves, the ASUS ZenFone 8 Flip stands out as a beacon…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing Samsung SmartThings In a world where technology continues to evolve, Samsung SmartThings emerges as a beacon of innovation,…
Read More
Exploring SEI Crypto: Redefining the Landscape of Digital Finance Understanding SEI Crypto SEI Crypto emerges as a prominent player in…
Read More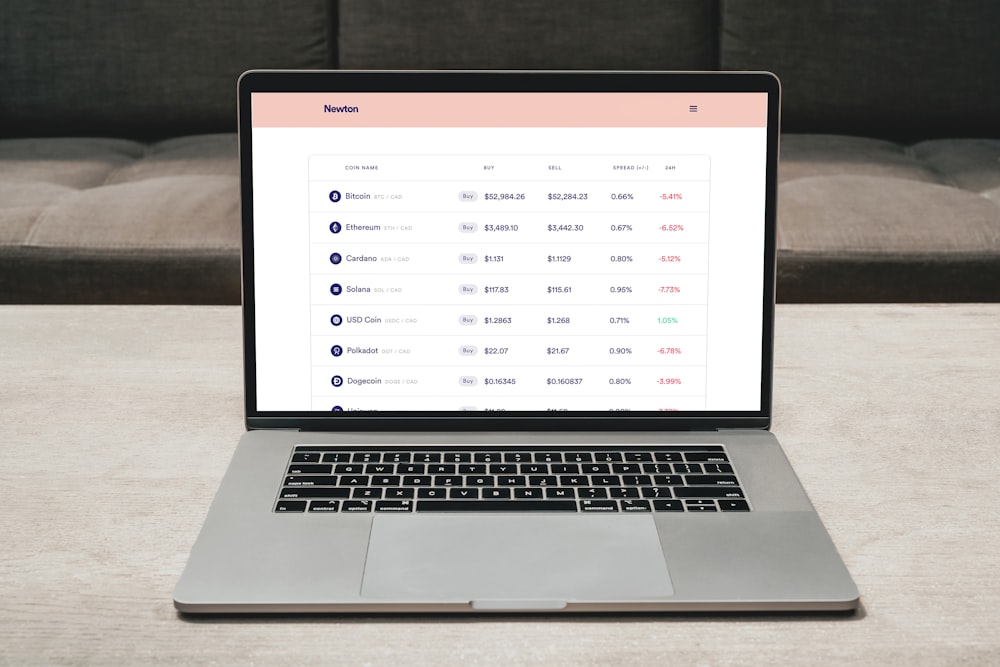
Unveiling the Story of Sejarah Metaverse A Journey Through Digital Realms The concept of Sejarah Metaverse has captured the imagination…
Read More
Mastering Python Learning: Essential Tips for Success Navigating the Python Learning Journey Embarking on the journey to learn Python can…
Read More
Introducing the Samsung Galaxy A22 Affordable Brilliance In the ever-evolving world of smartphones, finding a device that offers a perfect…
Read More
Introduction: In the fast-paced world of smartphones, Nokia has always been a name synonymous with quality and innovation. With the…
Read More
Introducing the Samsung Galaxy A10e Affordable Excellence In a world where smartphones seem to be getting more expensive by the…
Read More
Unlocking the Potential of Secret Network Crypto Understanding Secret Network Crypto Secret Network Crypto, often referred to simply as Secret…
Read More
Radiant Blockchain: Illuminating the Future of Digital Transactions Pioneering Innovation in Digital Finance In the ever-evolving landscape of digital finance,…
Read More
Unbeatable Android Phone Deals Limited Time Offer! In today’s fast-paced world, staying connected has become more important than ever. With…
Read More
Dive into the Colorful World of Slime Storytime Unlocking Creativity: The Magic of Slime In the realm of storytelling, few…
Read More
Introduction: The Samsung Galaxy A03s Unveiled In the ever-evolving landscape of smartphones, Samsung continues to impress with its latest release,…
Read More
Introduction: In today’s fast-paced world, music has become an integral part of our daily lives. Whether we’re commuting to work,…
Read More
Subheading: Introducing the Apple Watch SE Nike Edition In the fast-paced world of fitness technology, Apple and Nike have once…
Read More
Exploring the Influence of Scarlett TikTok The Rise of Short-Form Video Platforms In recent years, short-form video platforms like Scarlett…
Read More
RTFKT Nike Acquisition Price Revealed: What Does it Mean for Sneaker Culture? A Game-Changer in the Sneaker World The recent…
Read More
Unveiling the Musical Journey of Sheena Melwani From YouTube Sensation to Musical Star Sheena Melwani has captivated audiences worldwide with…
Read MoreKey Takeaways: Professional tree services are indispensable for sustaining and improving urban greenery and public safety. Routine maintenance ensures trees…
Read More
Mastering Python Efficiency Unleashing the Power of Python In the realm of programming, Python stands out as one of the…
Read More
Unveiling Shibarium: The Future of Blockchain Technology A New Era Dawns In the fast-paced world of blockchain technology, innovation is…
Read More
Exploring the Luxurious Realm of SK VIP Virtual Space Introduction: Unveiling the Digital Oasis In a world increasingly defined by…
Read More
Exploring the Legacy of Rodger Cleye Introduction: The Visionary Leader Rodger Cleye, a name synonymous with innovation and success, has…
Read More
Exploring the Boundless Realms of SKT Ifland: A Journey into Virtual Wonderland Introduction: The Gateway to Virtual Adventure SKT Ifland…
Read More
Exploring the Boundless Realms of the Real Metaverse In the vast expanse of digital landscapes, the concept of the real…
Read More
The Early Days: A Glimpse into Quinton Griggs’ Beginnings Quinton Griggs, a name now synonymous with digital influence, had humble…
Read More
Exploring Shiba Inu Blockchain: Unraveling the Potential Introduction: Shiba Inu and Blockchain In the world of cryptocurrency, Shiba Inu has…
Read More
Unveiling Sia Blockchain: Revolutionizing Data Storage A Game-Changing Innovation In the fast-paced world of technology, innovation is the driving force…
Read More
Elevate Your Lifestyle with Smart Life HomeKit Introducing Smart Life HomeKit: A Gateway to Modern Living In the fast-paced world…
Read More
Speed Up Python Loops with List Comprehensions Mastering Array Manipulation in JavaScript When it comes to manipulating arrays in JavaScript,…
Read More
Embarking on an Adventure: Navigating Snapchat’s Metaverse Introduction Welcome to the exciting world of Snapchat’s Metaverse, where reality blends seamlessly…
Read More
Unveiling Scott Stornetta: The Architect of Blockchain The Genesis of Blockchain Scott Stornetta stands as a towering figure in the…
Read More
Mastering Python for Competitive Programming Understanding the Landscape In the world of competitive programming, mastering Python can be a game-changer.…
Read More
Shibarium Blockchain: Redefining Decentralized Finance Introduction: The Rise of Shibarium Blockchain In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, Shibarium has…
Read More
Unveiling Sienna Mae Gomez: The Rising Social Media Star Introduction: Sienna Mae Gomez has taken the social media world by…
Read More
Enhance Your TikTok Experience with SnapTik Online In the ever-evolving landscape of social media, TikTok has emerged as a dominant…
Read More
Unlocking the Power of SmartIR Home Assistant Introducing SmartIR Home Assistant: A Game-Changer in Home Automation In today’s fast-paced world,…
Read More
Deciphering the Trend: Salty Ice Cream TikTok Meaning Understanding the Phenomenon Salty Ice Cream TikTok has taken social media by…
Read More
Unleash Your Python Skills with Clever Code Tricks Mastering Python Efficiency In the world of programming, mastering Python efficiency is…
Read More
Introduction Cryptocurrency has evolved significantly since the inception of Bitcoin over a decade ago. While Bitcoin laid the foundation, numerous…
Read More
Mastering Python Programming Tricks: Boosting Your Efficiency Navigating the Python Programming Landscape Python, renowned for its simplicity and versatility, is…
Read More
Mastering the Setup: HomePod Mini Unveiled The Unboxing Experience Unboxing your new HomePod Mini is a moment of anticipation and…
Read More
Revolutionizing Cryptocurrency: SafeMoon Blockchain A New Era in Digital Finance SafeMoon Blockchain has emerged as a disruptive force in the…
Read More
Exploring the Advancements in Sirin Labs Finney: A Game-Changer in Mobile Security Introduction: Redefining Mobile Security with Sirin Labs Finney…
Read More
Exploring Quorum Crypto: Revolutionizing Digital Transactions The Evolution of Quorum Crypto In the fast-paced world of digital finance, Quorum Crypto…
Read More
Immersive Adventures Await with Reality Pro VR Headset Exploring the World of Virtual Reality In recent years, virtual reality (VR)…
Read More
Exploring the Digital Oasis of SK VIP Virtual Space Unlocking the Gateway to the Future In the ever-expanding landscape of…
Read More